Identification of Differentially Expressed Long Noncoding RNAs and mRNAs Involved with Dominant Follicle Selection in Goats using RNA-seq
Identification of Differentially Expressed Long Noncoding RNAs and mRNAs Involved with Dominant Follicle Selection in Goats using RNA-seq
Guang-Xin E1, Yong-Ju Zhao1, Yue-Hui Ma2, Ming-Xing Chu2, Jia-Hua Zhang1, Zhong-Quan Zhao1, Hui-Jiang Gao2, Huai-Zhi Jiang3, Di Liu4, Li Liu5, Yan-Bin Zhu6, Wang-Dui Basang6, Luo-Bu Danjiu7, Tian-Wu An8, Xiao-Lin Luo8, Shi-Cheng He7 and Yong-Fu Huang1,*
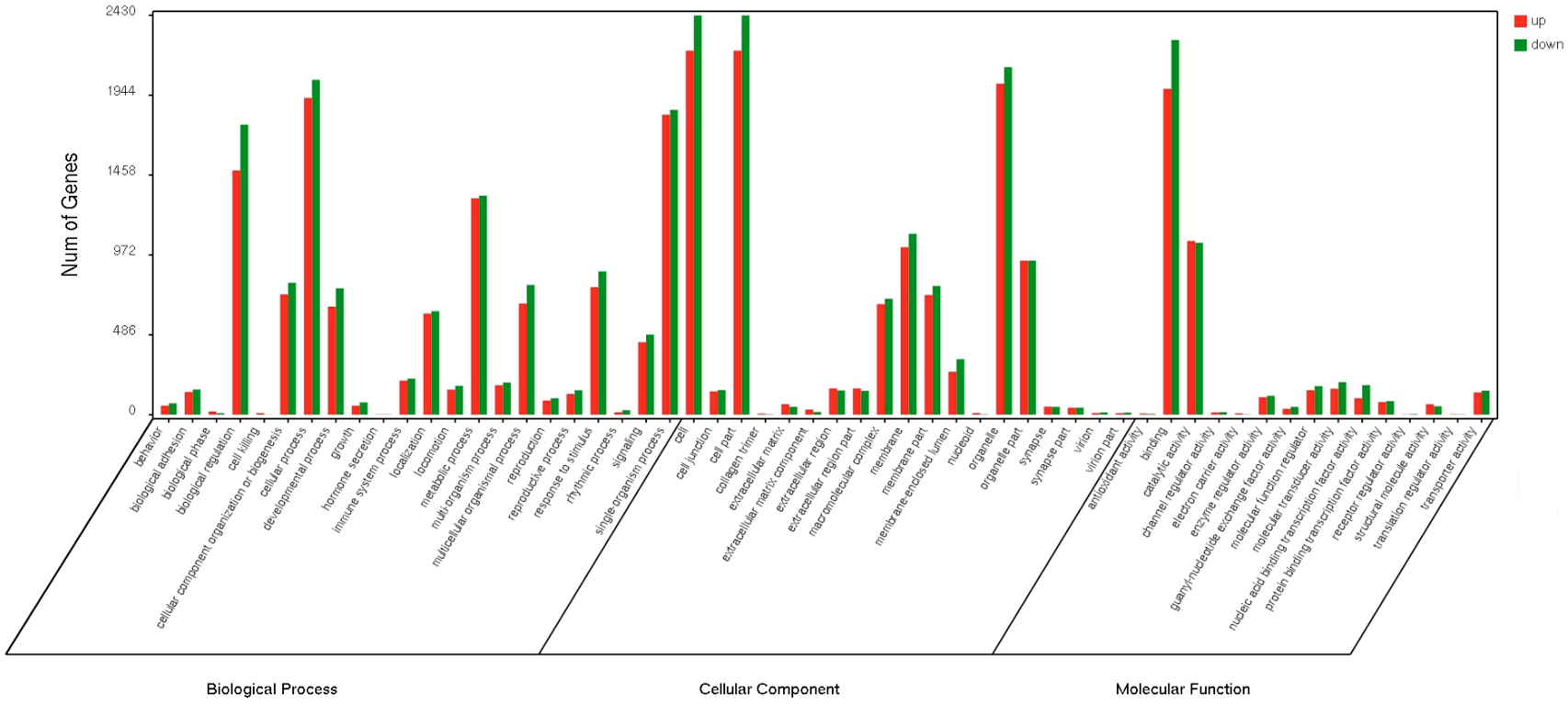
Differential expressed gene distribution of gene ontology (GO) categories (level 2) of dominant and indominant follicles mixed pools for goat. GO functional annotations are summarized in three main categories: biological process, cellular componentand molecular function.
Top20 enriched pathway of differential expressed coding gene between dominant and indominant follicles in goat.
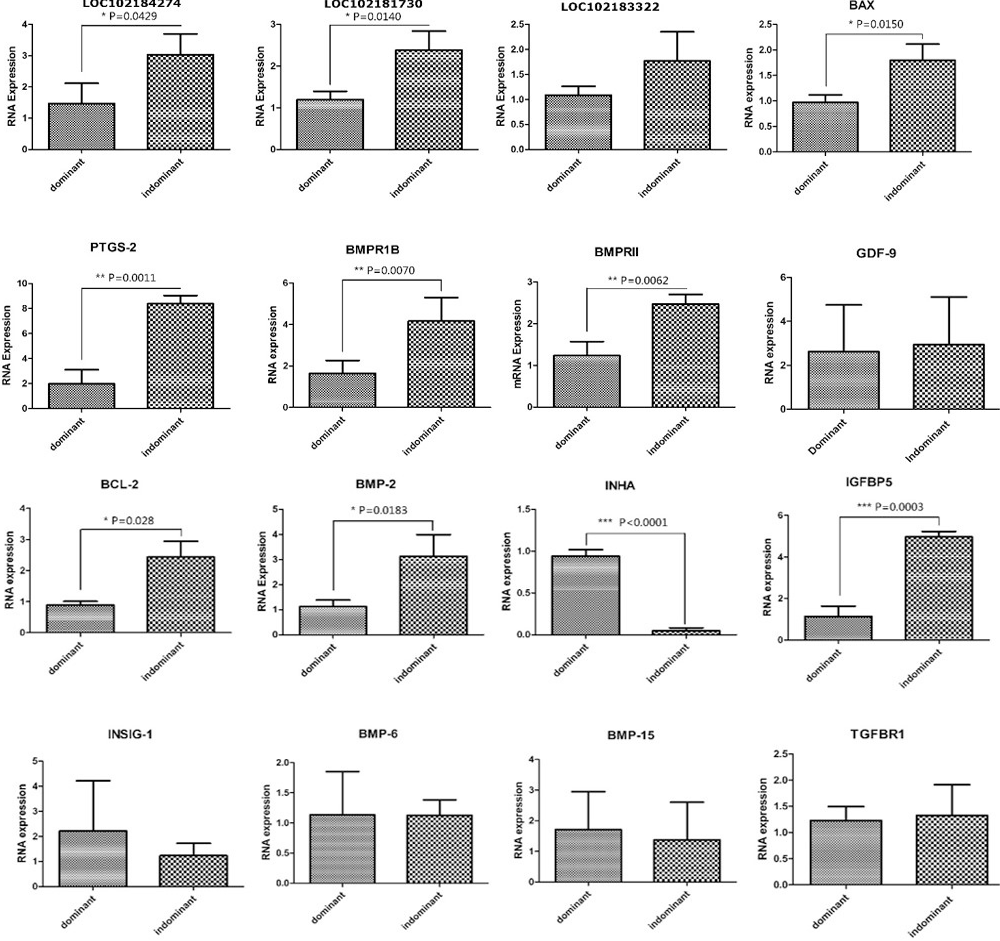
Candidate transcripts expression pattern of dominant and indominant follicles in goat using q-PCR.
Real time PCR validation of differentially expressed genes and long nocoding RNA in dominant and indominant follicles. Abundance of target genes was normalized relative to abundance of GAPDH gene. Bars in each panel represent the mean ± standard error (sample number = 3 and 3 parallel repetition per sample), * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. BMPR1B, IGFBP5, PTGS-2, BMP2, IGFBP5, BMPR1B, LOC102181730, LOC102184274, LOC102183322 were significant up-regulated expressed in NF in compare with DF; BAX, BCL2, INHA, INSIG were significant up-regulated expressed in DF in compare with NF, which identified from RNA-seq.