Immunohistochemical Localization of Leptin and Leptin-Receptor Proteins in Different Tissues of Chinese Alligator, Alligator sinensis
Immunohistochemical Localization of Leptin and Leptin-Receptor Proteins in Different Tissues of Chinese Alligator, Alligator sinensis
HuaBin Zhang1,2, YaSen Li1, Tao Pan1, Peng Yan1, En Li1, Hui Xue1 and XiaoBing Wu1,*
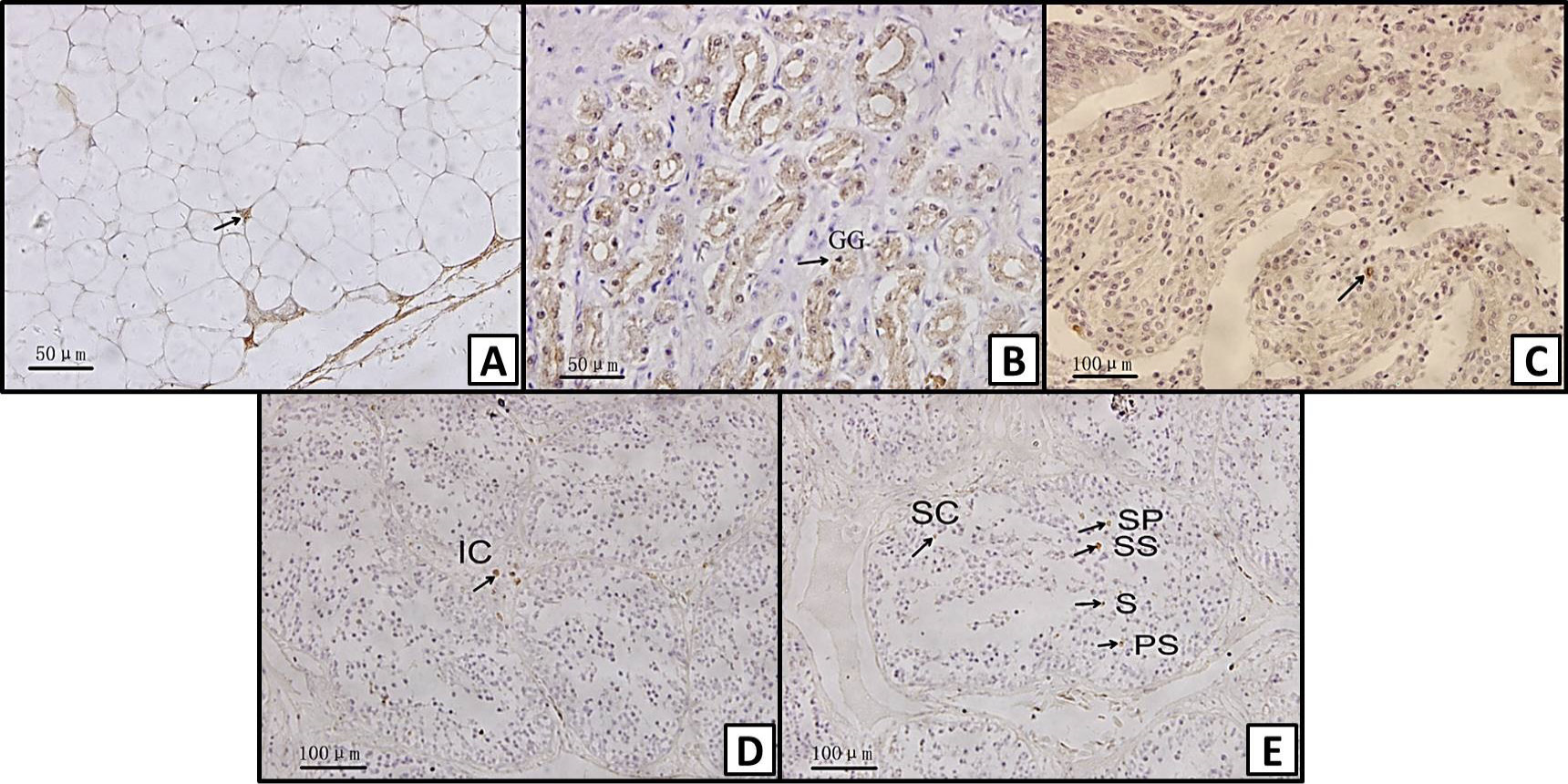
Immunohistochemical localization of leptin in different tissues of Chinese alligator: A, adipocyte; B, gastric gland (GG) of the stomach; C, lamina propria of the intestine; D, interstitial cell (IC) of the testis; E, supporting cell (SC), spermatogonium (SP), primary spermatocyte (PS), secondary spermatocyte (SS), and spermatid (S) of the testis. Magnification: A, B, C = X400; D, E = X200.
Immunohistochemical localization of leptin receptor in different tissues of Chinese alligator: A, adipocyte; B, submucosa (SUI) and muscular layer (ML) of the intestine; C, intestine villi (IV) of the intestine; D, granulosa cell (G) and follicular membrane cell (FM) of the ovary; E, submucosa (SUS) of the stomach; F, gastric gland (GG) of the stomach; G, interstitial cell (IC), seminiferous tubule (ST) of the testis. Magnification: A, C, E = X400; B, D, F, G = X200.
The difference in leptin of male and female Chinese alligator in different months. (values are expressed as mean ± SE).