Physiological and Histological Changes in Crayfish Procambarus clarkii after Acute Temperature Stress
Physiological and Histological Changes in Crayfish Procambarus clarkii after Acute Temperature Stress
Yi Zhao1,2,3, Lei Luo1,2, Liqi Tan4, Jianhua Huang1,2, Dongliang Liu1,2,5, Shigui Jiang1,2 and Lishi Yang1,2*
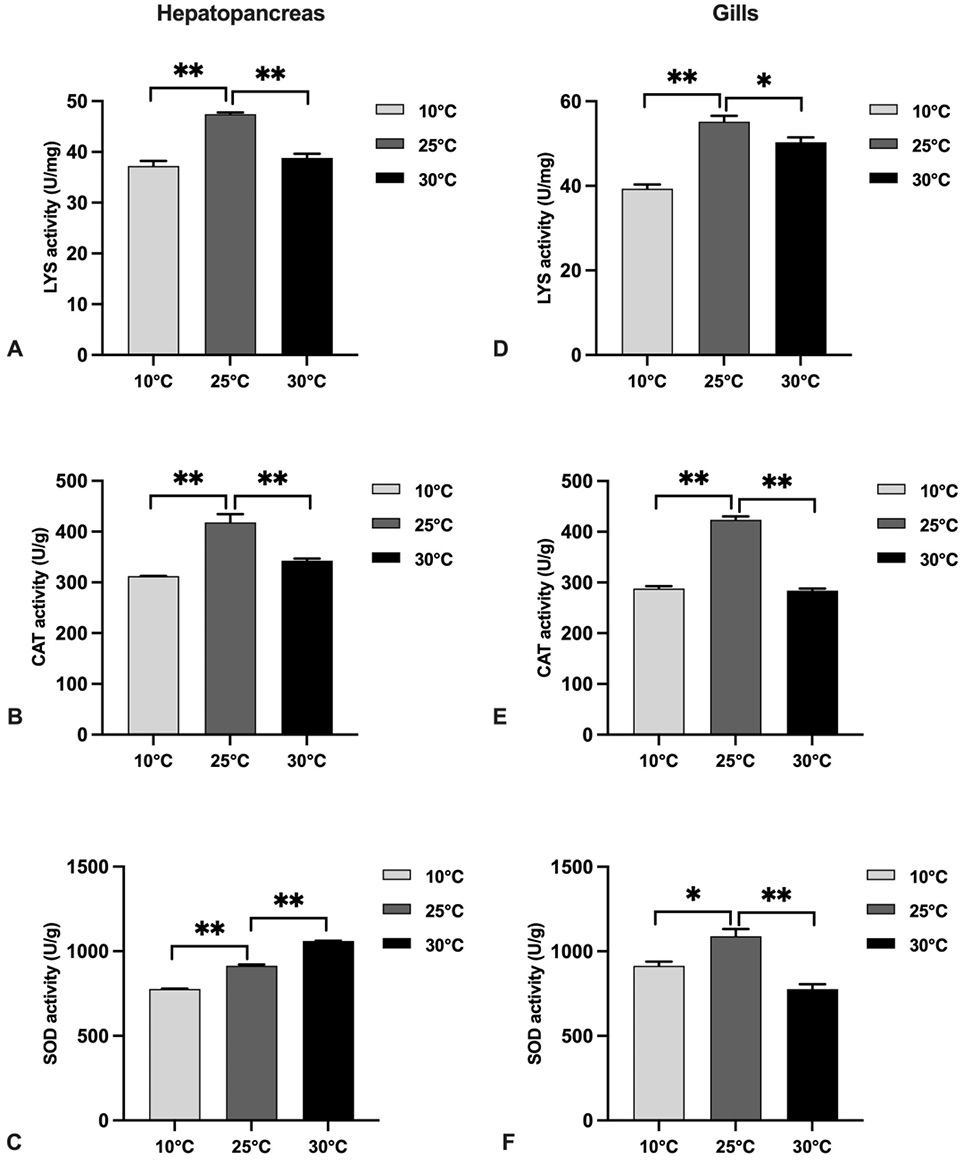
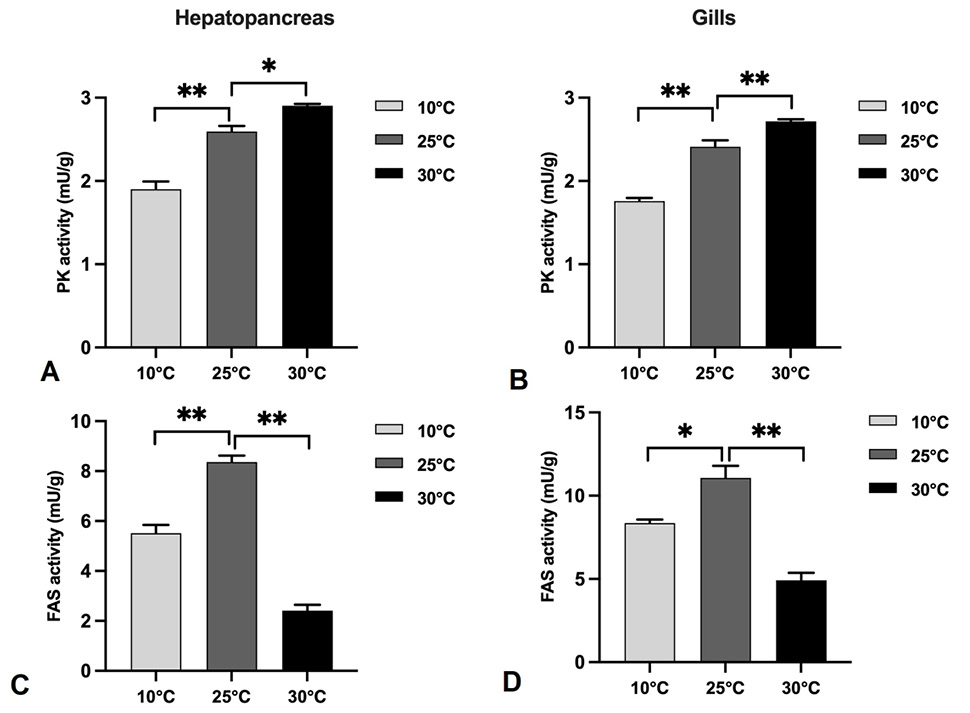
Effect of different temperature on LYS (A, D), CAT (B, E) and SOD (C, F) activities of hepatopancreas (A, B, C) and gills (D, E, F) of P. clarkii.
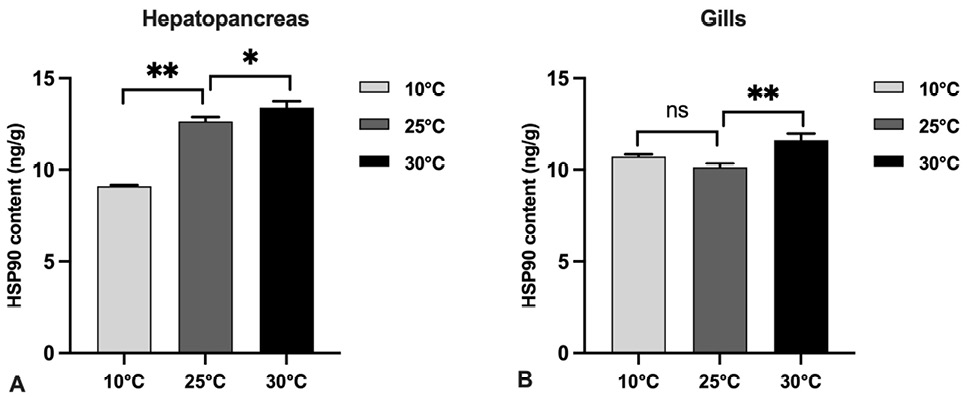
Effect of different temperature on HSP90 contents of hepatopancreas (A) and gills (B) of P. clarkii.
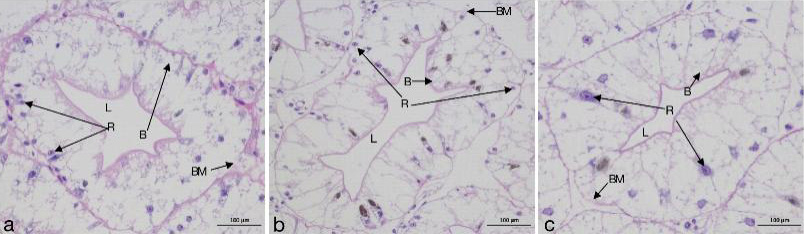
Effect of acute temperature stress on histological structure of hepatopancreas of cray fish. (a: 10°C, b: 25°C, c: 30°C) on the microstructure of the hepatopancreas of P. clarkii. B, secretory cells; R, storage cells; L, hepatopancreas tubules Lumen; BM, basement membrane. Stain: Hematoxylin & Eosin. Magnification 400X.