Role and Regulatory Mechanism of LGR5 in the Occurrence and Development of Breast Cancer
Role and Regulatory Mechanism of LGR5 in the Occurrence and Development of Breast Cancer
Yajuan Zheng, Qiuping Mo, Hongchao Tang, Qinghui Zheng and Dandan Guan*
(A) The results of Western blot analysis of the expression of LGR5 and IQGAP1 in human breast cancer, including the original gel image and the relative value of LGR5 and IQGAP1 (phosphorylated/non-phosphorylated). The symbol * means p < 0.05 compared to Tumor group. (B) The results of immunohistochemical analysis of LGR5 and phosphorylated IQGAP1 expression in breast cancer.
(A) The results of Western blot analysis of the expression of LGR5 and phosphorylated IQGAP1 (pSer(IP)) in human normal breast cell line, metastatic human breast cancer cell line and LGR5-knockdowned MDA-MB-231 cell line, including the original gel image and the relative values of LGR5 and pSer(IP). The symbol * means p < 0.05 compared to Parental and Vector groups. (B) The results of CCK8 assay analyzing the relative cell viability of the three cell lines after 24 h of culture. The symbol * means p < 0.05 compared to MDA-MB-231 group. (C) The results of cell scratch test to analyze the migratory ability of cells in the three cell lines. (D) The results of transwell detection to analyze the invasive ability of cells in the three cell lines.
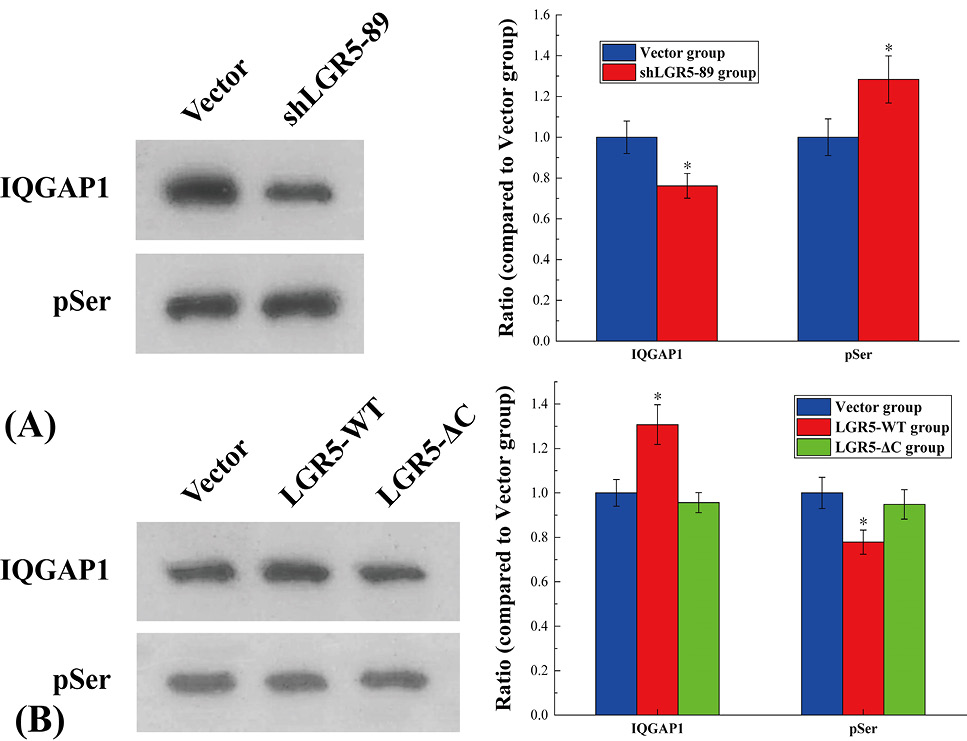
The results of immunoprecipitation to detect the reaction between LGR5 and IQGAP1. (A) Relative expression levels of IQGAP1 and phosphorylated IQGAP1 in LoVo cell lines and cell lines after LGR5 knockout. The symbol * means p < 0.05 compared to Vector group. (B) Relative expression of IQGAP1 and phosphorylated IQGAP1 in LoVo cell line, LGR5 overexpressing cell line and LGR5-ΔC (lack of C-terminal tail) overexpressing cell line. The symbol * means p < 0.05 compared to Vector group.