Testing the Contact and Residual Toxicity of Selected Low-Risk Pesticides to Tetranychus Urticae Koch and its Predators
Testing the Contact and Residual Toxicity of Selected Low-Risk Pesticides to Tetranychus Urticae Koch and its Predators
Riaz Shah1* and Margaret Appleby2
Percent mortality caused by several pesticides to adult female Tetranychus urticae 72 hours after treatment by Potter tower (Direct spray F=79.6, df=7, p<0.001; Spray residues F=19.7, df=7, p<0.001). Means followed by the same letter between same bar type are not statistically different, LSD (p<0.05).
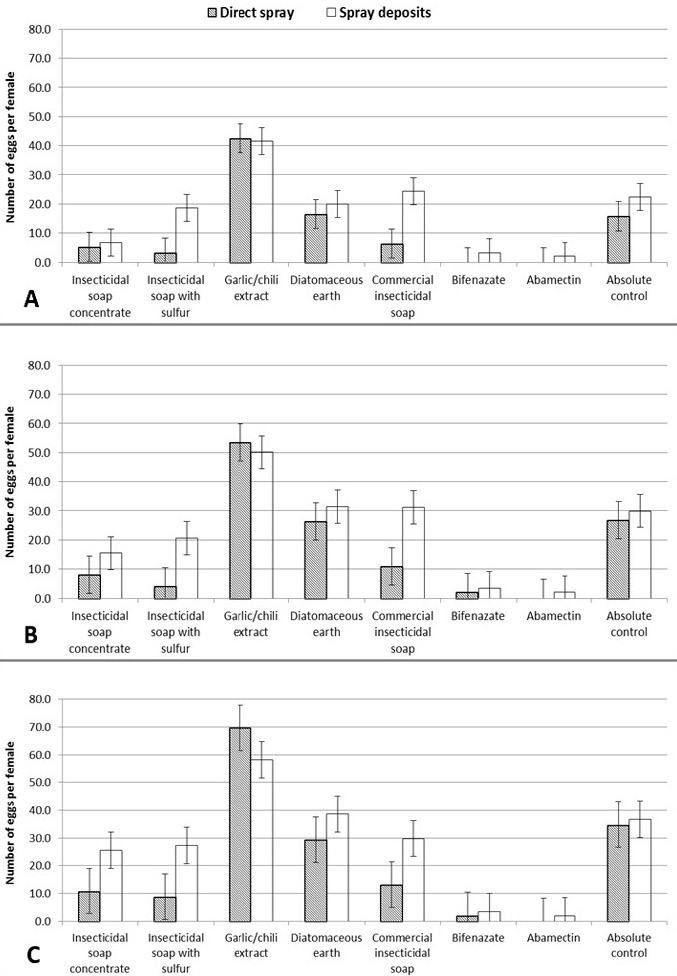
Number of eggs (+se) laid by a single Tetranychus urticae female in 24 (A), 48 (B) and 72 (C) hours after treatment with several pesticides (Direct spray F=4.36, df=7, p=0.006; Spray residues F=5.24, df=7, p=0.006). Means followed by overlapping standard error between same bar type are not statistically different.