Biochemical Profiling of Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Impaired Carbohydrate Metabolism and its Therapeutic Intervention via Modulation of Metabolic Pathways
Biochemical Profiling of Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Impaired Carbohydrate Metabolism and its Therapeutic Intervention via Modulation of Metabolic Pathways
Muhammad Sajid Hamid Akash1*, Hina Sharif1, Kanwal Rehman2, Sumbal Rasheed1 and Shagufta Kamal3
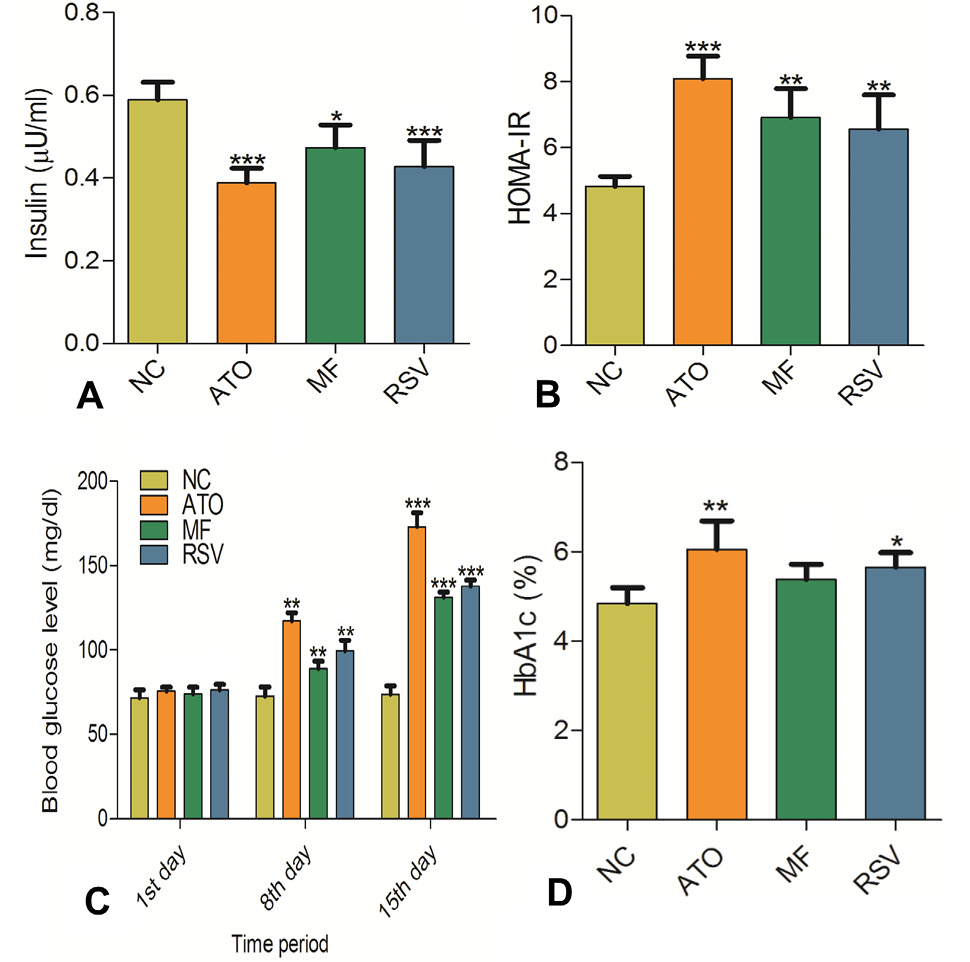
Arsenic concentration in the liver sample is detected by HG-AAS. For statistical details and abbreviations, see Figure 1. *** represents P < 0.001 when compared with NC group. As, arsenic; HG-AAS, hydride generation atomic absorption spectroscopy.