Biochemical and Histopathological Changes Associated with Fasciola spp. in Slaughtered Buffaloes at Al-Muthanna Province, Iraq
Biochemical and Histopathological Changes Associated with Fasciola spp. in Slaughtered Buffaloes at Al-Muthanna Province, Iraq
Hussein Jabar Jasim1*, Amer Murhum Al-Amery2
Gross examination of infected liver with Fasciolosis showed cirrhosis and paleness of the liver and enlargement of bile ducts.
Gross examination of infected liver with Fasciolosis showed congestion with multiples abscesses formation on the hepatic capsule.
Gross examination of infected liver with Fasciolosis showed Calcified of the bile ducts and fibrinous exudates.
Gross examination of infected gallbladder with Fasciolosis showed congested and dilated full of density matter of bile juice.
Histopathological section of liver showing; A: destruction of liver tissue; B: thickening of bile duct; C: fibrosis proliferation in the portal area; D: coagulative necrosis of liver cell; E: parasitic tract formed from destructed hepatocytes intermixed with infiltrated inflammatory cell (H & E stain. X10).
Histopathological section of liver showing; A: fatty change; B: coagulative necrosis; C: hemorrhage; D: fibrous connective tissue capsule; E: Kupffer cells (H & E stain. X20).
Histopathological section of liver showing; A: dilated sinusoids; B: coagulative necrosis of hepatocytes; C: fibrosis of portal area; D: migratory tract with inflammatory cell infiltration. (H & E stain. X20).
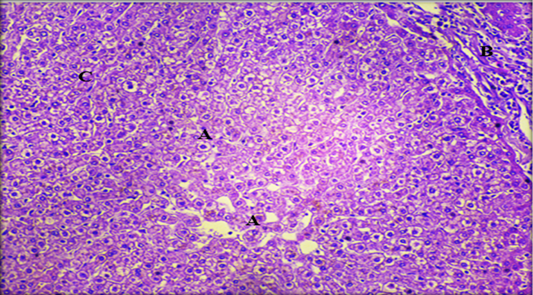
Histopathological section of liver showing, A: hypertrophy of hepatocytes; B: fibrosis of portal area with infiltration inflammatory cells; C: kupffer cells (H & E stain. X20).
Histopathological section of liver showing A: hyperplasia of bile duct which proliferation of the epithelial lining as gland, B: fibrosis of portal area with infiltration inflammatory cells, C: hemosiderin (Yellowish brown materials accumulated among hepatocytes in bile canaliculi, D: kuffper cells (H & E stain. X20).
Histopathological section of gallbladder showing A: necrotic tissue; B: destruction of glands; C: fibrosis of mucosa; D: aggregation of lymphocytes cells and E: hemorrhage (H & E stain. X10).