Corn Substitution Through Na-Glutamate and Neurospora Species Supplementation in Cassava and Tofu Dregs
Corn Substitution Through Na-Glutamate and Neurospora Species Supplementation in Cassava and Tofu Dregs
Munasik*, Titin Widiyastuti, Caribu Hadi Prayitno
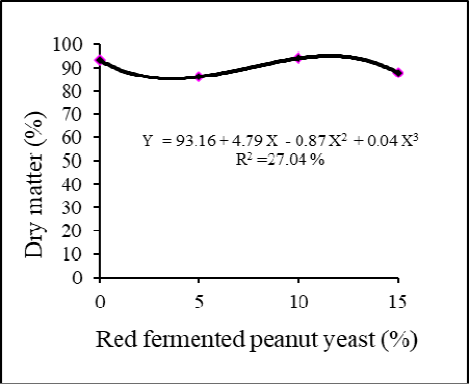
Moisture of post fermented cassava-tofu dreg.
Effect of red fermented peanut cake yeast addition on the crude fiber of post fermented cassava-tofu dreg.
Effect Na-glutamate on the crude fat.
Effect of red fermented peanut cake yeast addition on the inorganic matter of post fermented cassava waste-tofu dreg.
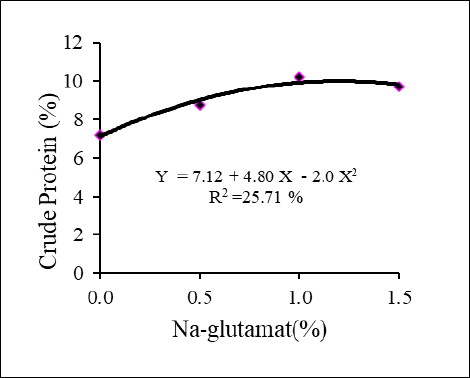
Effect of Na-glutamate on the crude protein.
Effect of red fermented peanut cake yeast on the crude protein.
Effect of Na-glutamate on the NFE.
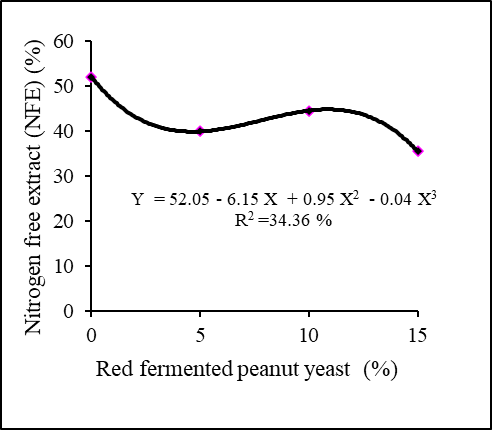
Effect of red fermented peanut cake yeast addition on the NFE.
Calcium concentration of post-fermented cassava waste-tofu dreg with Na-glutamate level (A) and red fermented peanut cake yeast level (B).
Phosphor concentration of post-fermentation cassava waste tofu dreg with Na-glutamate level (A) and red fermented peanut cake yeast level (B).
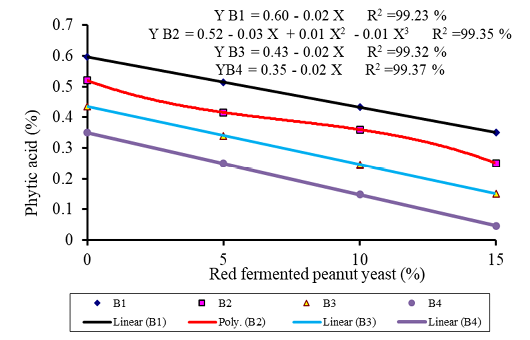
Cassava waste-tofu dreg phytic acid content post-fermentation with different levels of Na-glutamate (A) and level of red fermented peanut cake yeast (B).