Dual Role of Multicopper Oxidase of Klebsiella pneumoniae as a Copper Homeostatic Element and a Novel Alkaline Laccase with Potential Application in Green Chemistry
Dual Role of Multicopper Oxidase of Klebsiella pneumoniae as a Copper Homeostatic Element and a Novel Alkaline Laccase with Potential Application in Green Chemistry
Soumble Zulfiqar1, Khuram Shehzad1, Sana Tahir1, Khalid A. Al-Ghanim2 and Abdul Rauf Shakoori1,2,3,*
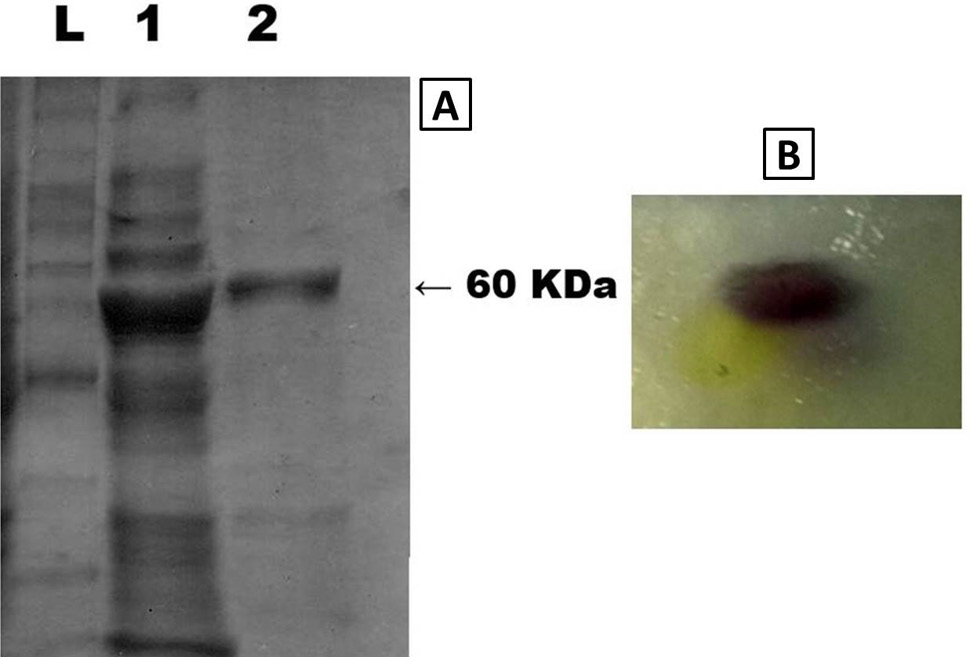
A, Lane L, Novex unstained protein ladder, (10494-0/2); Lane 1, IPTG induced supernatant; Lane 2, Purified CueO protein. B, Zymogram for activity assay of purified CueO protein.
CueO of K. pneumoniae KW is an active enzyme exhibiting laccase like activity. A, the enzyme activity was determined against some phenolic substrates in respective buffer systems across a range of pH. The optimum activity for SGZ and DMP was found at pH 6.5 and 8, respectively; B, CueO activity with various metal ions as co-factors depicted that Cu is the sole cofactor for CueO amongst the ones used in the experiment.
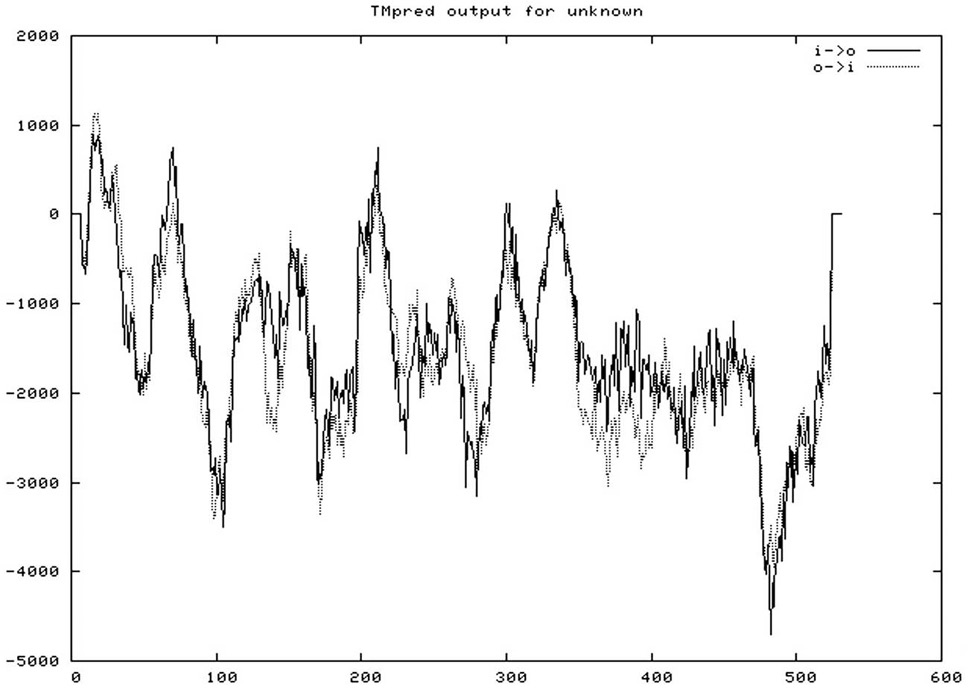
Two transmembrane helixes predicted in CueO run inside to outside (i-o) and the other way as well.
BLAST search predicted sequence alignment reveals highly conserved regions between CueO and other multi copper oxidases reported in literature.
The CueO core sequence has been conserved in all lines of species in evolutionary discourse which depicts its multiple functionality nature as reported in literature.
A, I-TASSER predicted 3D model of CueO KW without copper centers. B, active centre microenvironment prediction of CueO. Green balls, trinuclear copper cluster; Blue labels, histidine residues coordinating with copper ion.
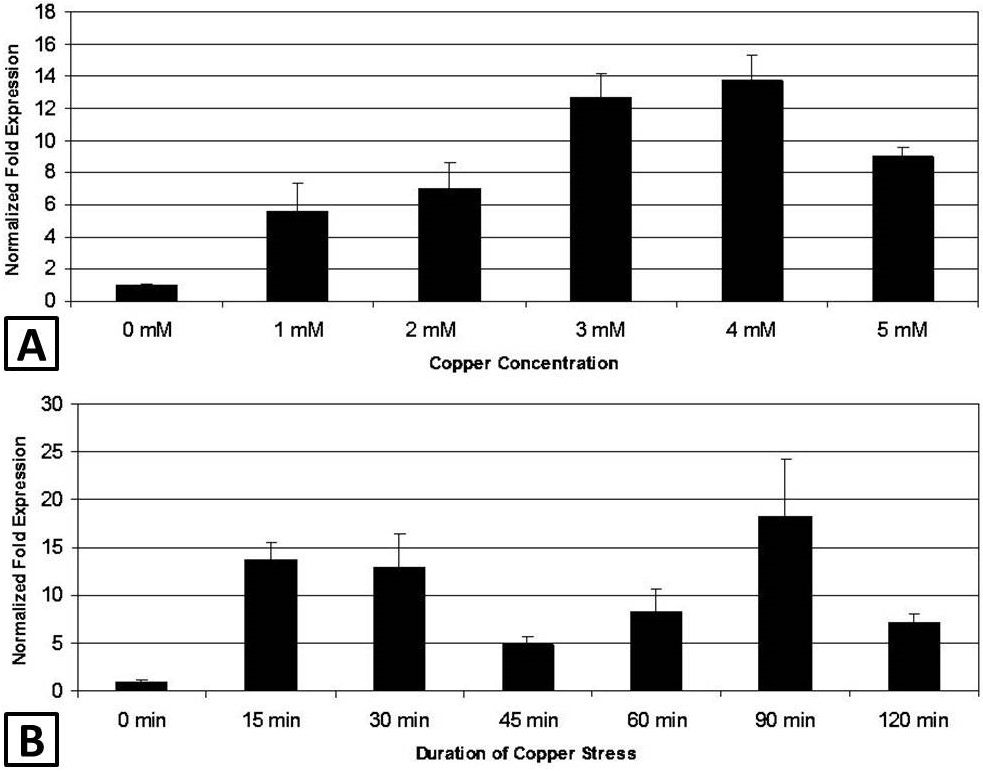
Relative quantification of CueO mRNA level of K. pneumoniae KW in response to Cu+2. A, bacterial cultures (20 ml) were grown and Cu+2 stress ranging 0 to 5mM was given at early log phase stage. Total RNA isolated was subjected to RT PCR. cDNA synthesized were used for real time PCR. RNA level in each sample normalized to GyrA (housekeeping gene) were quantified in relation to that in control (0mM Cu+2). A gradual increase in CueO mRNA was observed up to 4 mM Cu+2 that decreased with further increase in medium Cu+2; B, RNA level was measured with respect to Cu+2 exposure time in the presence of 4 mM Cu+2. A bimodal increase in CueO mRNA level was found with two maxima, first at 15 and 30 min and second at 90 min.