Effective Management of Ginger Soft Rot Caused by Penicillium digitatum through Plant Extracts
Effective Management of Ginger Soft Rot Caused by Penicillium digitatum through Plant Extracts
Qaiser Shakeel1*, Rabia Tahir Bajwa1, Yasir Iftikhar2, Mustansar Mubeen2, Muhammad Luqman3, Waqas Ashraf1 and Ifrah Rashid4
Comparison of control treatment with different plant extract for the inhibition of mycelial growth of Penicillium digitatum where; (a) garlic extract (100mg/mL), (b) Control plate (c) moringa extract (100mg/mL).
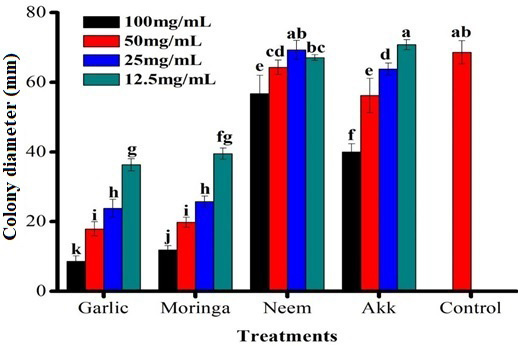
Effect of plant extract on the mycelial inhibition of Penicillium digitatum.
Comparison of control treatment with different fungicides for the inhibition of mycelial growth of Penicillium digitatum where; (a) Ridomil Gold (1000ppm), (b) Control plate and (c) Anthem (1000ppm).
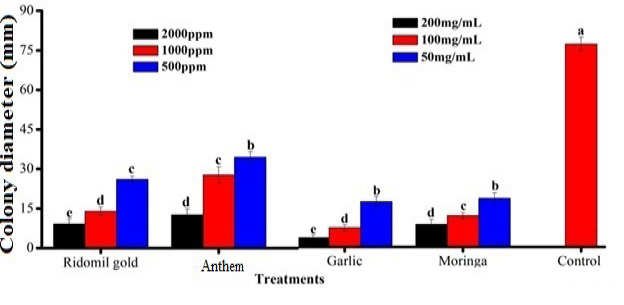
Effect of fungicides on the mycelial inhibition of Penicillium digitatum.
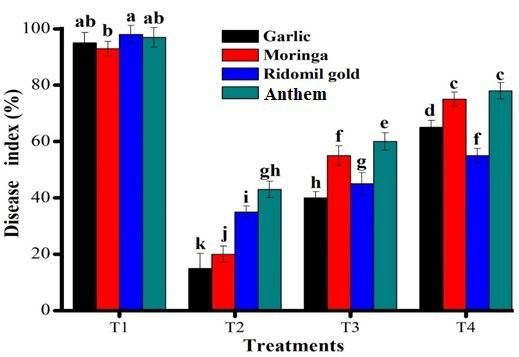
Assessment of effect of treatment time of different plant extract and fungicides on Penicillium digitatum disease index on ginger.
Comparison between effects of different plant extract and fungicides on the mycelial inhibition of Penicillium digitatum on ginger.