Ganoderma lucidum as a Biocontrol agent for Management of Alternaria solani, A Pathogen of Early Blight of Tomato
Ganoderma lucidum as a Biocontrol agent for Management of Alternaria solani, A Pathogen of Early Blight of Tomato
Muhammad Asif1*, Ahmad Ali Shahid1,2 and Nasir Ahmad3
A) Purigied mycelial growth, B) Microphotograph of conidial strutures of Alternatia solani on PDA at 100x (Labomed CXL, Labo America inc.)
A) Basidiocatp, B) Mycelial growth, C) Hmenium, D) Basidiospores of G. lucidum.
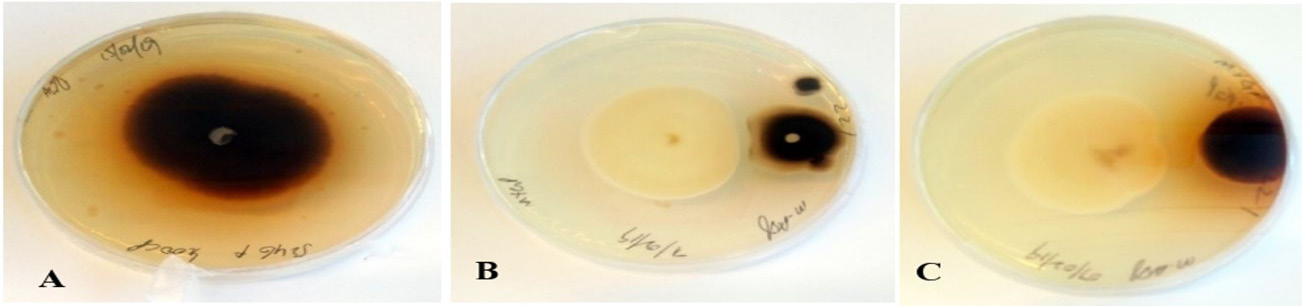
Antagonistic effect of G. lucidum against A. solani; A) Control (A. solani) B anc C) Dual culture (G. lucidum in white colony and A. solani in black colony showing growth zone of inhibition).
Activity assay of crude protein extract aginst A. solani. Different alphabet letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 probability level.
Antigungal potential of crude protein extract of G. lucidum agaist A. sonani. A) Control, B) 0.5mg/ml, C)1mg/ml, D) 2mg/ml.
MIC of crude protein against A. solani by using Microspectropotmetry. Different alphabet letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 probability level.