Genetic Analysis of An Giang Ongole Cattle Based on Mitochondrial DNA D-Loop, Y Chromosomal Haplotypes and Polymorphism of Genes Associated with Economic Traits
Genetic Analysis of An Giang Ongole Cattle Based on Mitochondrial DNA D-Loop, Y Chromosomal Haplotypes and Polymorphism of Genes Associated with Economic Traits
Nguyen Ba Trung1,2*, Pham Thi Kim Phuong1,2
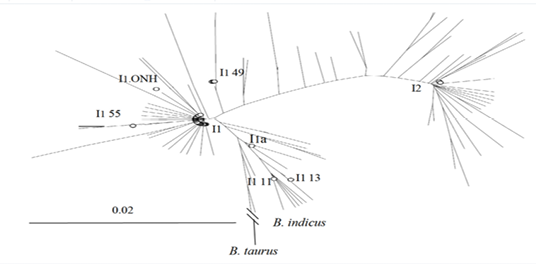
Phylogenetic tree of Ongole cattle* (*Constructed based on 240 bp mtDNA of 127 sequences, including 30 An Giang Ongole cattle and 97 sequences of indigenous cattle in South Asia, China, Southeast Asia, and Europe, using the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method by MEGA11 software. Eight haplotypes observed in An Giang Ongole cattle are represented by circles).
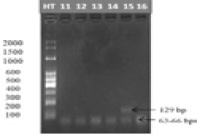
The NCAPG gene was cut by the Tsp509I enzyme in samples 11-16. Well HT: Standard DNA ladder (2,000, 1,500, 1,000, 600, 500, 400, 300, 200, and 100 bp).
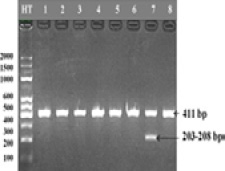
Cutting the DGAT1 gene with the EaeI enzyme in samples 1-8. Well HT: Standard DNA ladder (2,000, 1,500, 1,000, 600, 500, 400, 300, 200, and 100 bp).
The RNF212 gene has been cut by the AlwI enzyme in samples 1 and 2. Well HT: Standard DNA ladder (2,000, 1,500, 1,000, 600, 500, 400, 300, 200, and 100 bp).