Improving the Efficiency of Campylobacter spp. Isolation from Livestock and Poultry in Ukraine
Improving the Efficiency of Campylobacter spp. Isolation from Livestock and Poultry in Ukraine
Natalia Shchur1,2*, Tetiana Mazur1, Orest Katsaraba3, Ihor Halka2, Ludmila Shalimova2, Larisa Moskalenko4, Tetiana Ponomariova-Herasymiuk4, Maksym Lusta4, Vitalii Nedosekov1
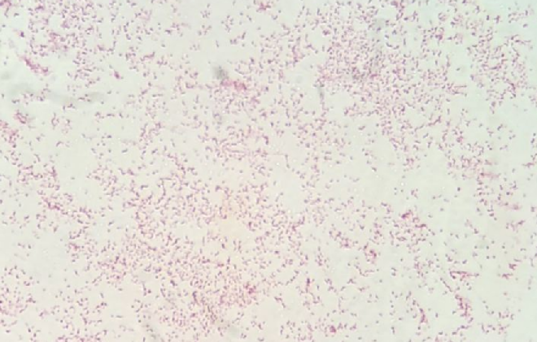
Campylobacter spp. in mixed culture. Gram-negative, thin, spirally curved bacteria that have one complete curl or resemble a ‘comma’ or ‘gull wings’. Gram stain. View under a Leica DM 5000 light microscope (immersion objective 100).
The results of isolation of Campylobacter spp. by the direct application method.
The results of isolation of Campylobacter spp. according to the enrichment method.
Cream colonies of Campylobacter spp. from a round shape with a shiny convex surface to the formation of a plaque on the surface of the medium with the effect of “swarming”. Campylobacter Agar, 24-hour cultivation.
Greyish colonies of Campylobacter spp. on mCCD agar from rounded shape with metallic sheen to formation of plaque on the surface of the medium with a “swarming” effect, 24-hour cultivation.
The cocci-like form of Campylobacter spp. Fuchsin staining. View under a Leica DM 5000 light microscope (immersion objective 100).