Isolation, Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Aspergillus flavus in Animal Feed
Isolation, Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Aspergillus flavus in Animal Feed
Dina Al-Shinawy1*, Reda E.M. Moghaieb2, Sara B. Awaly2, Gihan El-Moghazy1 and Dalia S. Ahmed2
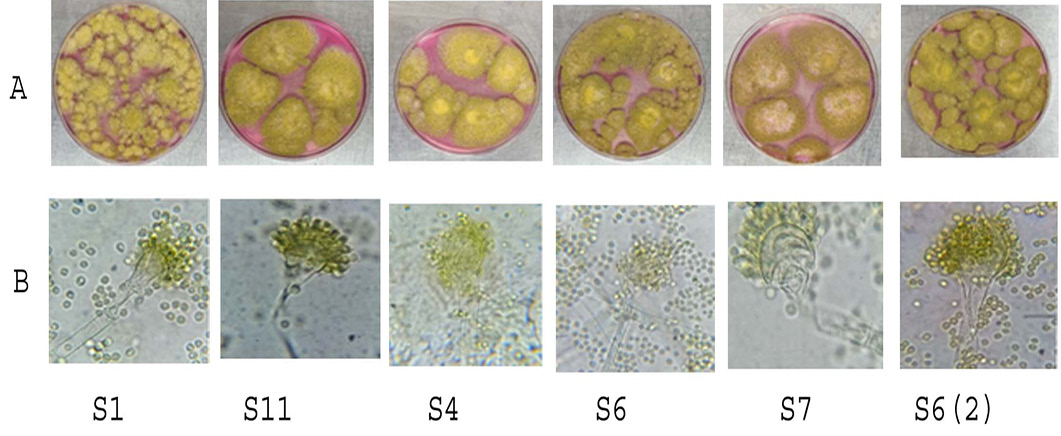
The major morphological of A. flavus isolates. A: Colonies on Rose Bengal agar at 25 °C typically consisted of a dense felt of yellow-green conidiophores, reaching a diameter of 3-5 cm in 5-7 d. B: Microscopic morphological characteristics: Conidial heads usually radiate, turning from yellow-green to dark yellow-green and then breaking into multiple loose columns. Hyaline and coarsely roughened conidiophores that can reach a length of 1.0 µm (with some isolates reaching 2.5 µm). Vesicles, 25-45 μm in diameter, which were globose to sub-globose.
Aflatoxin B (AFB) concentrations detected in the six Aspergillus flavus strains using the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) analysis. Error bars represent the standard deviation (±SD).
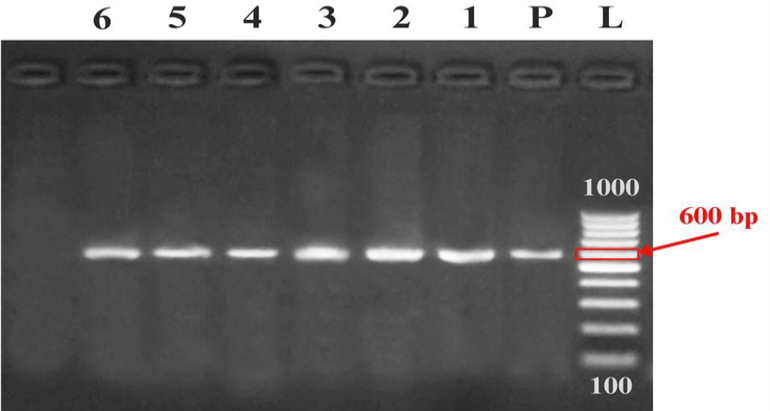
ITS region amplification of the six isolated Aspergillus flavus strains (lanes 1: S1, 2: S11, 3: S4, 4: S7, 5: S6-1, and 6: S6-2) demonstrating a single band at 600 bp of a 100 bp Ladder marker (L) and positive control (P).
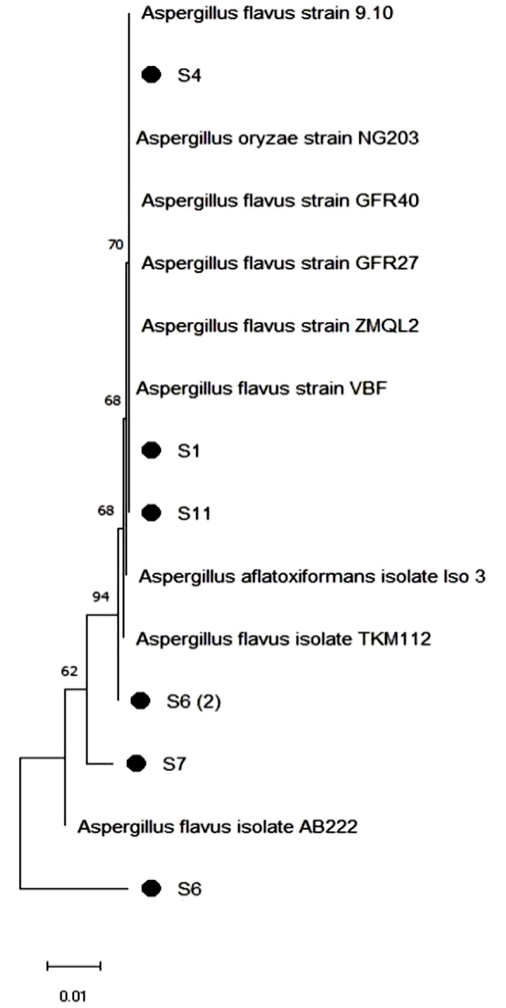
The NJ phylogenetic tree of six Aspergillus flavus strains with the closest hits in GenBank.
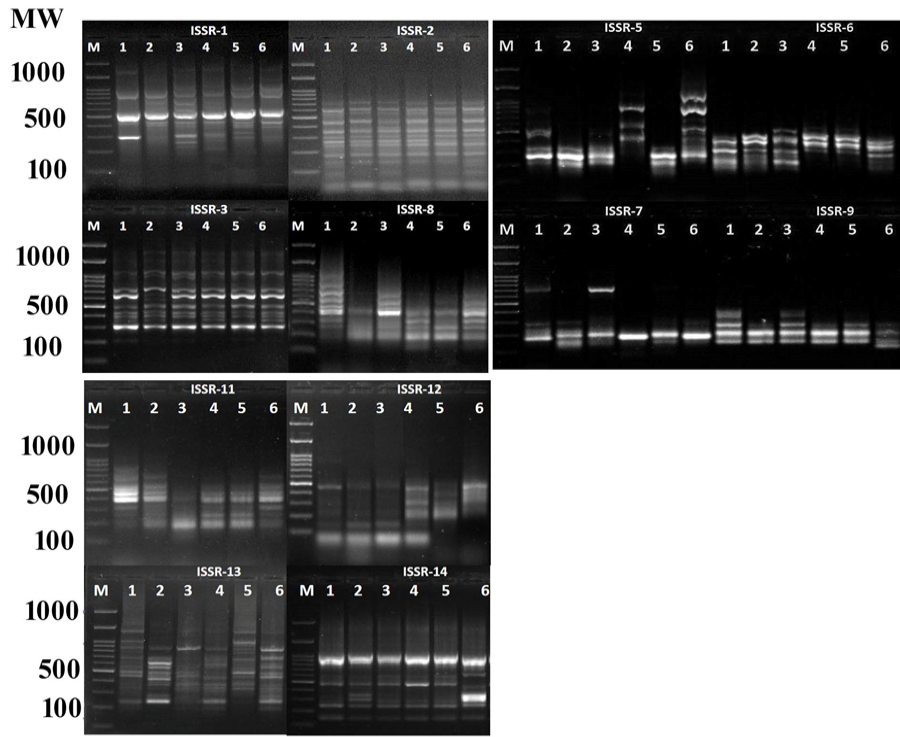
ISSR marker amplification of the six isolated Aspergillus flavus strains (lanes 1-S1, 2-S11, 3-S4, 4-S7, 5-S6-1, and 6-S6-2) and M- 100 bp Ladder marker.
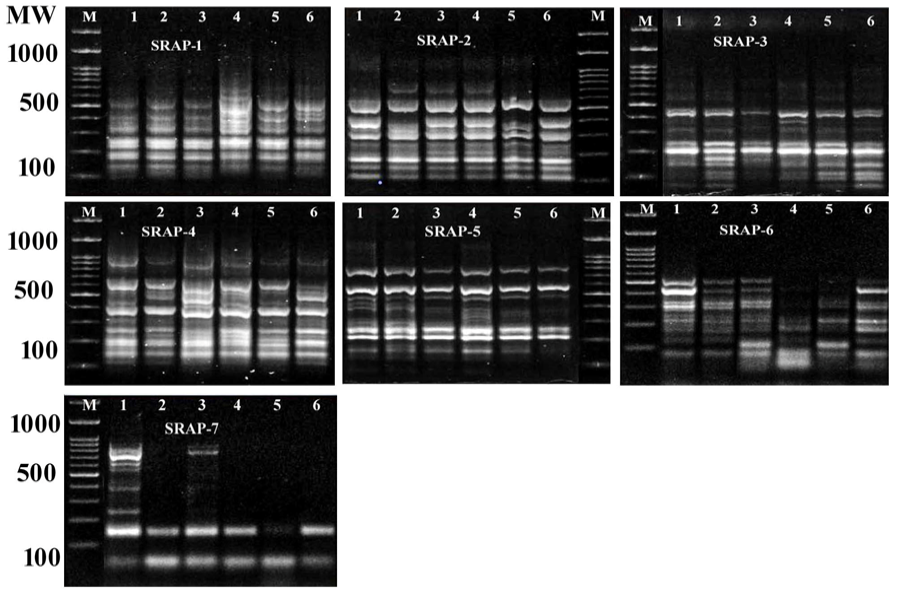
SRAP marker amplification of the six isolated Aspergillus flavus strains (lanes 1-S1, 2-S11, 3-S4, 4-S7, 5-S6-1, and 6-S6-2) and M- 100 bp Ladder marker.
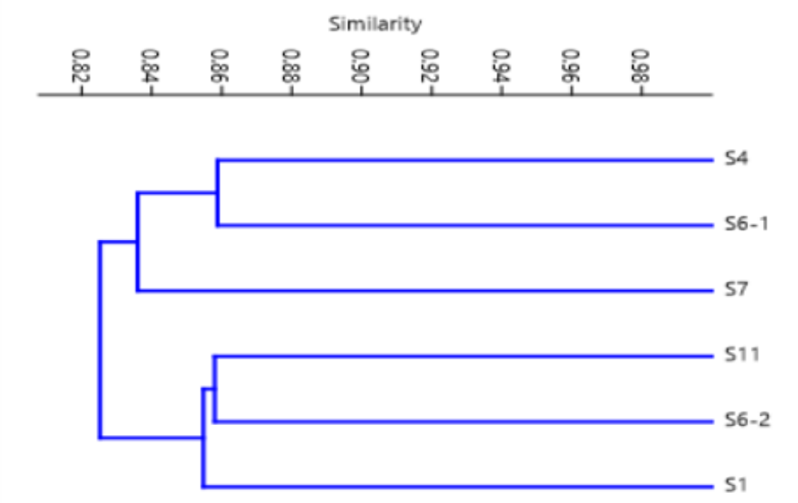
Phylogenetic tree of the six Aspergillus flavus strains based on pooled ISSR-SRAP markers.