Metabolic Engineering of Berberine in Plants Can Confer Resistance to Insects
Metabolic Engineering of Berberine in Plants Can Confer Resistance to Insects
Anila Latif, Zaheer Abbas, Farhatullah and Ghulam Muhammad Ali*
Isolation and cloning of BBE gene. a) Agarose gel electrophoresis of amplified product from DNA of B. lyceum; b) Agarose gel electrophoresis of pTZ57 R/T harboring BBE gene.
Developments of plant transformation construct. a) Agarose gel electrophoresis of entry clone isolated from transformed colonies; b) Agarose gel electrophoresis of plant transformation vector isolated from transformed colonies.
Physical map of complete cassette. LB, Left boarder; RB, Right boarder; CaMV 35S, Cauliflower mosaic virus 35 S promoter; YFP, Yeast fluorescent protein; BBE, Cloned barbarian bridge enzyme gene; P nose, P nose promoter; Pat, Phosphinothricin acetyle transferase gene; NOS, NOS terminator.
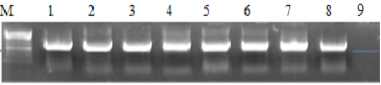
Transformation of Agrobacterium strain GV 3101 (pMP90RK). Lane M, 1kb DNA ladder (Fermentas); lane 1 and 2, 3 and 4 are amplified products from transformed colonies of Agrobacterium Lane 6 is non transformed colony.
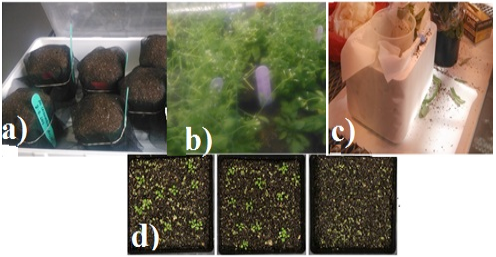
Different steps of floral dip transformation. a, Muffin preparation and seeds sowing; b, Maximum bolting stage prior to infection with transformed Agrobacterium; c, Infection with transformed Agrobacterium culture; d, Screening of transformants with basta spray.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of amplified products from transformed plants.
Expression analysis of BBE gene. Lane E1 to E9, amplifications of BBE gene from the reverse transcription reactions product from different transformed events; lane C, no amplification of BBE gene from the reverse transcription reaction product of wild type isogenic line. Lower panel shows the expression of 18S rRNA gene.
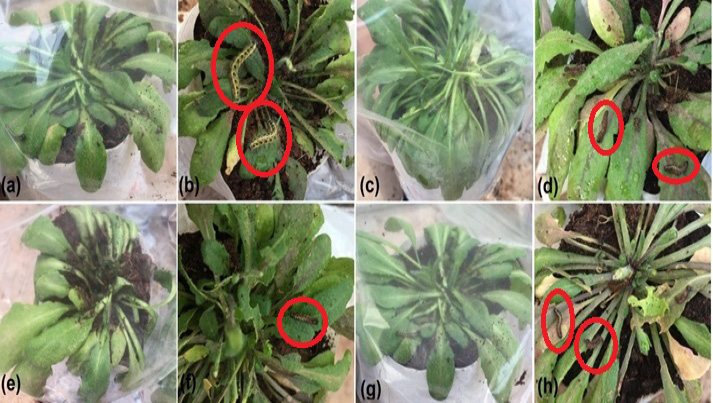
Insect bioassay of transformed and wild type isogenic line. a, wild type isogenic line exposed to 2nd instar larvae (photograph was taken just after introduction of larvae); b, wild type isogenic line (photograph was taken after 72 hours); c, e and g are transformed events 5, 8 and 9 respectively (photographs were taken just after introduction of insects); d, f and h are transformed events 5, 8 and 9 respectively (photographs were taken after 72 hours).