Molecular Detection of mecA Gene in Staphylococcus sp. Associated with Ruminant Mastitis
Molecular Detection of mecA Gene in Staphylococcus sp. Associated with Ruminant Mastitis
Hanan Yousif Jasim1*, Rasha Munther Othman2, Wasan Moaed Shaker3
Cow (A) and goat (B) with clear signs of mastitis (swelling and redness of udder).
Staphylococcus cultured on MSA (A) showing round, golden-yellow clusters and Gram stain (B).
Phylogenetic tree of analysis of Staphylococcus aureus: The genetic relationship of Phylogeny showing 9 local isolates of S. aureus isolated from different sources in Basrah and with other international strains that extracted from GenBank database. S litter denote to sample.
Phylogenetic tree of analysis of Staphylococcus sp.: The genetic relationship of Phylogeny showing 4 local isolates of Staphylococcus sp. bacteria isolated from different sources in Basrah and with other international strains that extracted from GenBank database. S litter denote to sample.
Phylogenetic tree of analysis of mecA gene in a local isolate: The sequence analysis of mecA genes in all 13 isolates were revealed 100% homology to the Staphylococcus aureus S286 DNA, Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec with ID number LC727174.1 and Staphylococcus aureus strain C249 chromosome with ID number CP127807.1. While 1 isolate only was shown 100% homology to the mecA gene that previously detected in Staphylococcus epidermidis strain 1FSE05 plasmid with ID: CP121525.1. S litter denote to sample.
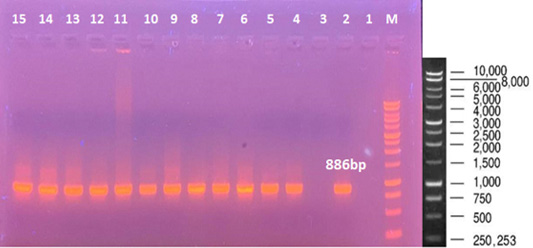
PCR amplification of 16S rDNA gene in 13 isolates of Staphylococcus sp. Lane 1 Negative control, Lane 3: mecA negative Staphylococcus sp. PCR product; Lanes 2 and 4-15: PCR products of Staphylococcus sp. isolates (527bp); M: 1kb DNA size marker.