Morphological and Immunophenotypical Properties of Chicken Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells Towards Wild Type and H5-Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Infections
Morphological and Immunophenotypical Properties of Chicken Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells Towards Wild Type and H5-Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Infections
Anis Suraya Mohamad Abir1, Sakinah Yusof1, Abd Rahaman Yasmin1,2, Abdul Rahman Omar1,3, Kok Lian Ho4, Wen Siang Tan1,5, Abdul Razak Mariatulqabtiah1,6*
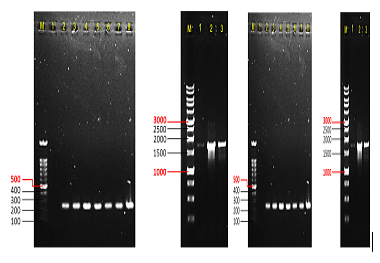
PCR products using (A) primer set FP9orf176 showing 240 bp expected band, whereby lanes (1) Negative control; (2) Positive control from original stock; (3) First CEF passage of WT FWPV infection; (4) Second CEF passage of WT FWPV infection; (5) Third CEF passage of WT FWPV infection; (6) First CEF passage of rFWPV-H5 infection; (7) Second CEF passage of rFWPV-H5; (8) Third CEF passage of rFWPV-H5; and (B) primer set H5 showing 1.7 kb expected band, whereby lanes (1) First CEF passage of rFWPV-H5 infection; (2) Second CEF passage of rFWPV-H5 infection; (3) Third CEF passage of rFWPV-H5 infection; M are ExactMark 100 bp or 1 kb DNA ladder marker, respectively (Base Asia). The DNA bands were observed in 1% (w/v) agarose gel.
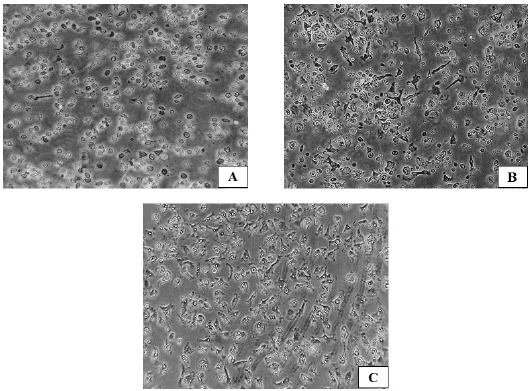
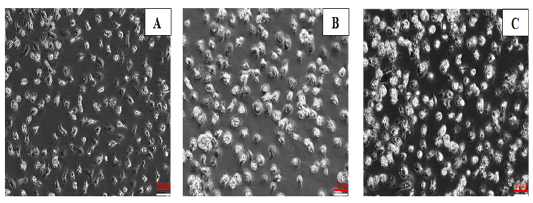
Morphological changes during generation and differentiation of chBM-DCs, on days 1 (A), 2 (B) and 3 (C) post seeding, using a Leica Microsystems inverted microscope. Magnification: 400X.
Morphologies of chBM-DCs for (A) non-infected control cells, (B) WT FWPV-infected cells, and (C) rFWPV-H5 infected cells, cultured in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-4, using a phase-contrast inverted microscope. Bar: 50 µm. Magnification: 200X.