Oviductus Ranae Improves Cognitive Disorder and Suppresses Oxidative Stress in Aging Mice by Activating Nrf2 Pathway
Oviductus Ranae Improves Cognitive Disorder and Suppresses Oxidative Stress in Aging Mice by Activating Nrf2 Pathway
Yuechen Li1, Yumo Li1, Xuefeng Zhuang1, Guangfu Lv2, Xiaowei Huang1, Zhe Lin1, Yuchen Wang1* and He Lin1*
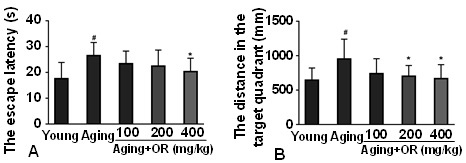
The effect of OR on the cognitive impairments in aging mice. (A) the escape latency and (B) the distance in the target. Notes: Compared with the young mice group, #P<0.05; compared with the aging mice group, *P<0.05.
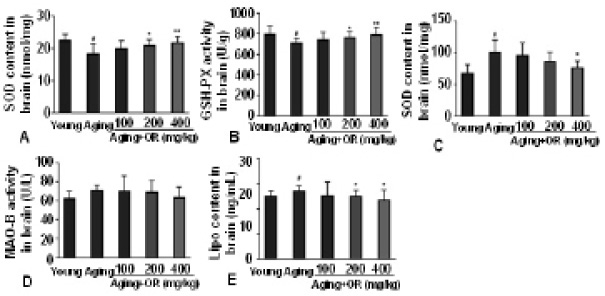
The effect of OR on oxidative stress in the hippocampus of aging mice. Activities of brain (A) SOD and (B) GSH-PX, (C) content of brain MDA, (D) activitys of brain MAO-B, (E) content of brain Lipo. Compared with the young mice group, #P<0.05; compared with the aging mice group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
The effect of OR on immune factors of aging mice. Content of serum (A) IgA, (B) IgG, (C) IgM, (D) IL-1 and (E) IL-2. Compared with the young mice group, #P<0.05; compared with the aging mice group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
The effect of OR on the Nrf2 pathway in aging mice. Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 expression were analyzed by western blot (A), Quantification graphs of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 are shown on (B), (C) and (D). Compared with the young mice group, #P<0.05; compared with the aging mice group, **P<0.01.