Skull Morphology of Four Species of Zokors (Rodentia, Myospalacinae)
Skull Morphology of Four Species of Zokors (Rodentia, Myospalacinae)
Yao Zou, Shien Ren, Miao Xu, Nannan Liang, Xuxin Zhang, Chongxuan Han and Xiaoning Nan
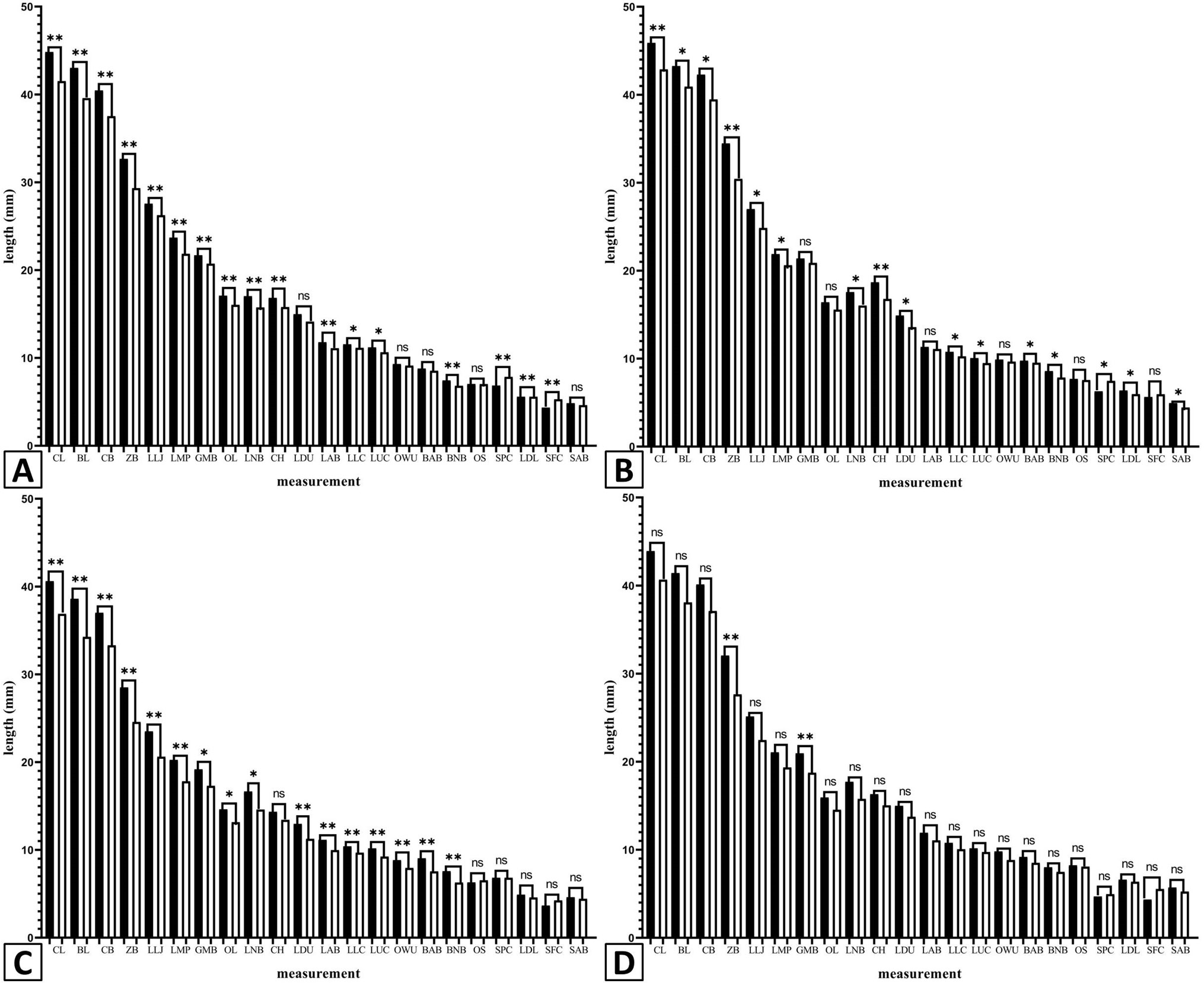
The skull differences between two sexes based on 22 skull morphological indexes. A, E. cansus; B, M. aspalax; C, E. rothschildi; D, E. baileyi. The samples in black and white represent males and females, respectively. * represents highly significant difference (p < 0.05); ** represents significant difference (p < 0.01) and ns represents no significant difference (p > 0.05).
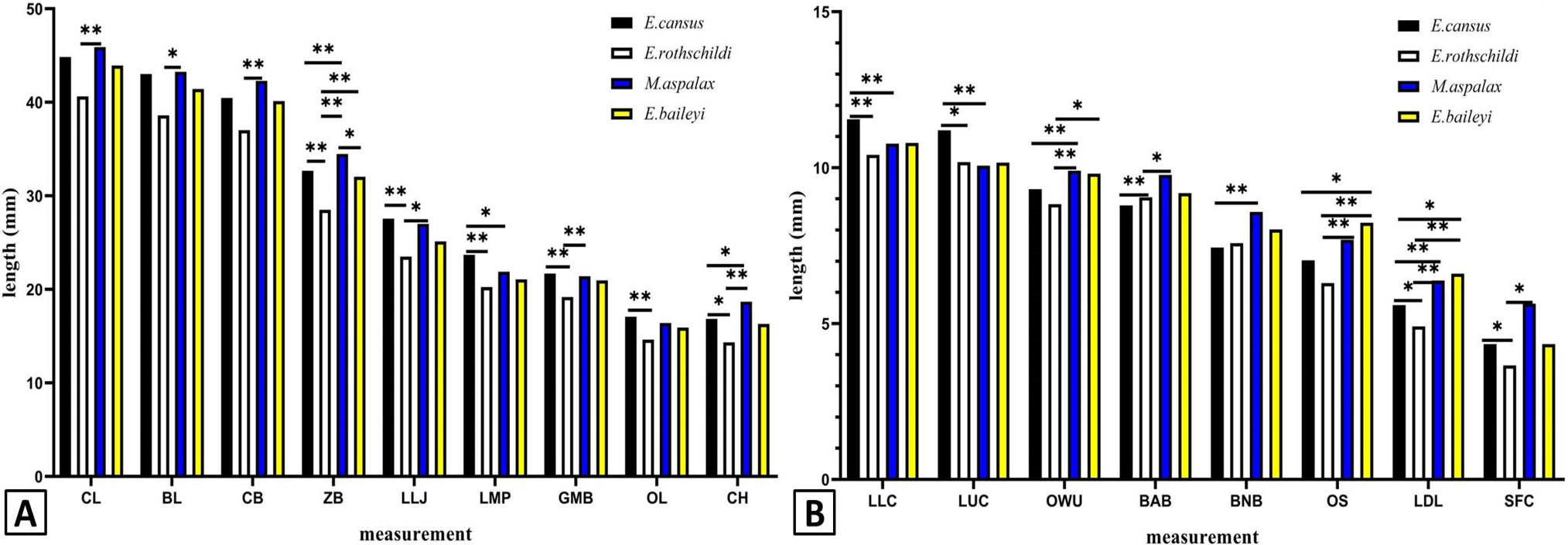
Skull differences of males among populations based on ANOVA and multiple comparison. A, CL, BL, CB, ZB, LLJ, LMP, GMB, OL, CH; B, LLC, LUC, OWU, BAB, BNB, OS, LDL, SFC. * represents highly significant difference (p < 0.05) and ** represents significant difference (p < 0.01).
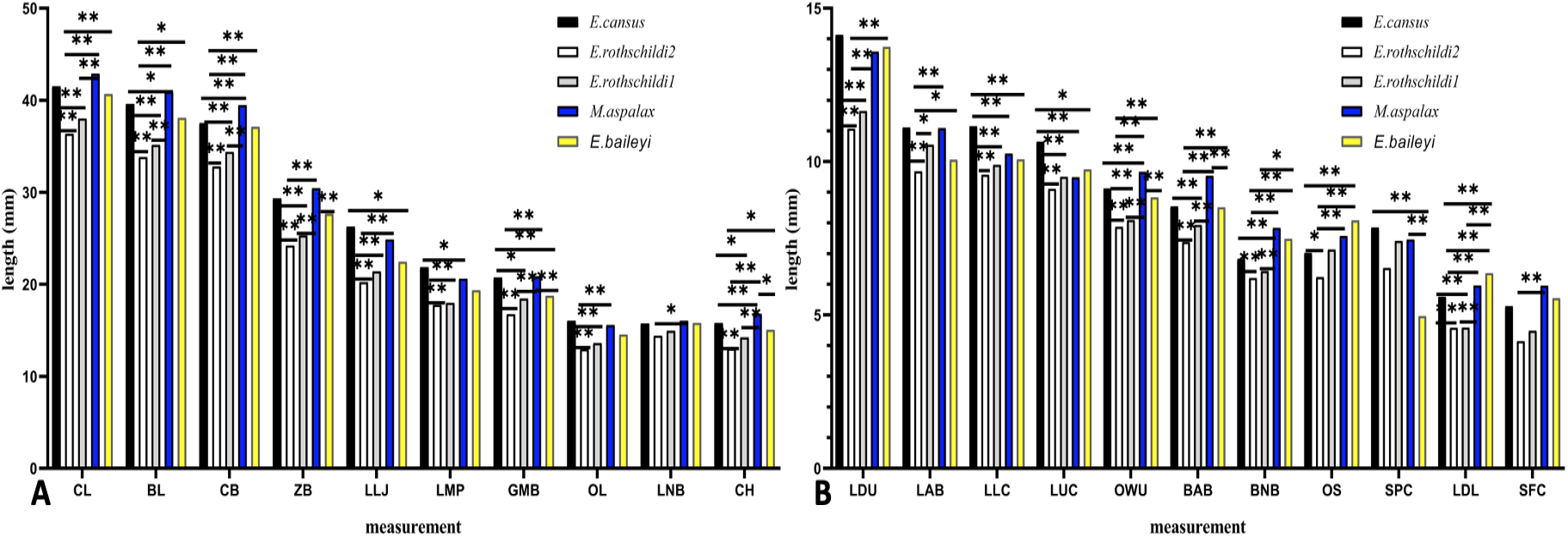
Skull differences of females among populations based on ANOVA and multiple comparison. A, CL, BL, CB, ZB, LLJ, LMP, GMB, OL, LNB, CH; B, LDU, LAB, LLC, LUC, OWU, BAB, BNB, OS, SPC, LDL, SFC. * represents highly significant difference (p < 0.05) and ** represents significant difference (p < 0.01).
Skull indexes clustering. A, males; B, females.
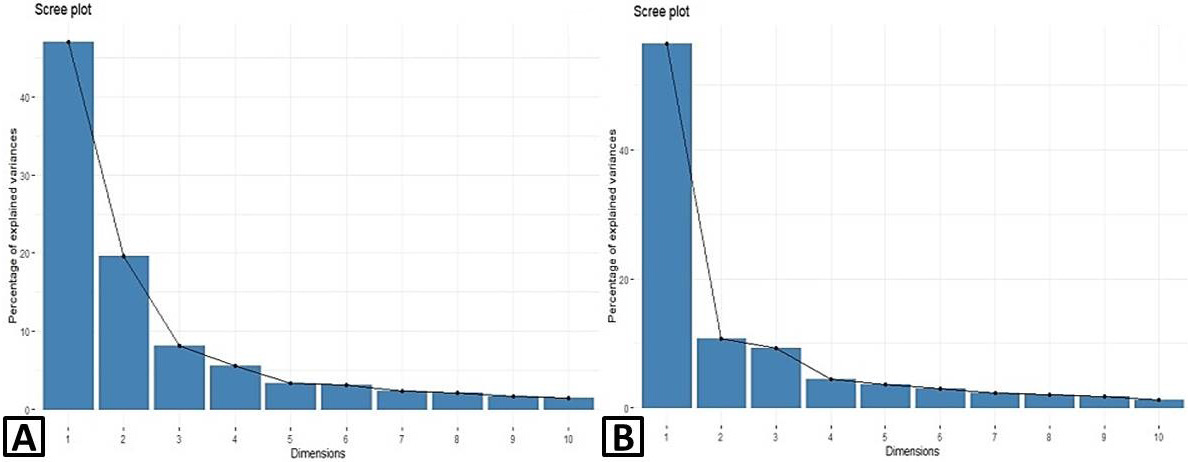
Contribution proportion of the first ten principal components. A, male; B, female.
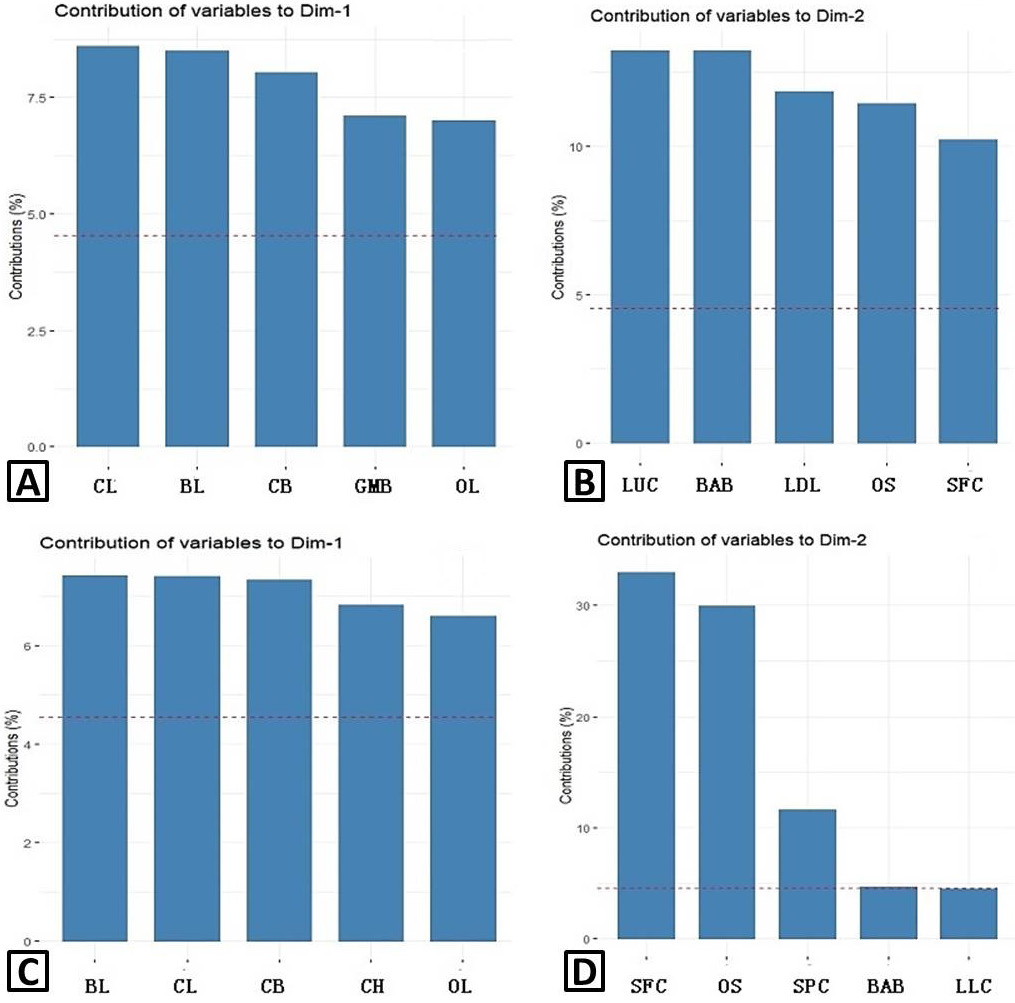
Contribution of variables to the first two principal components. A, male (variables to Dim-1); B, male (variables to Dim-2); C, female (variables to Dim-1); D, female (variables to Dim-2).
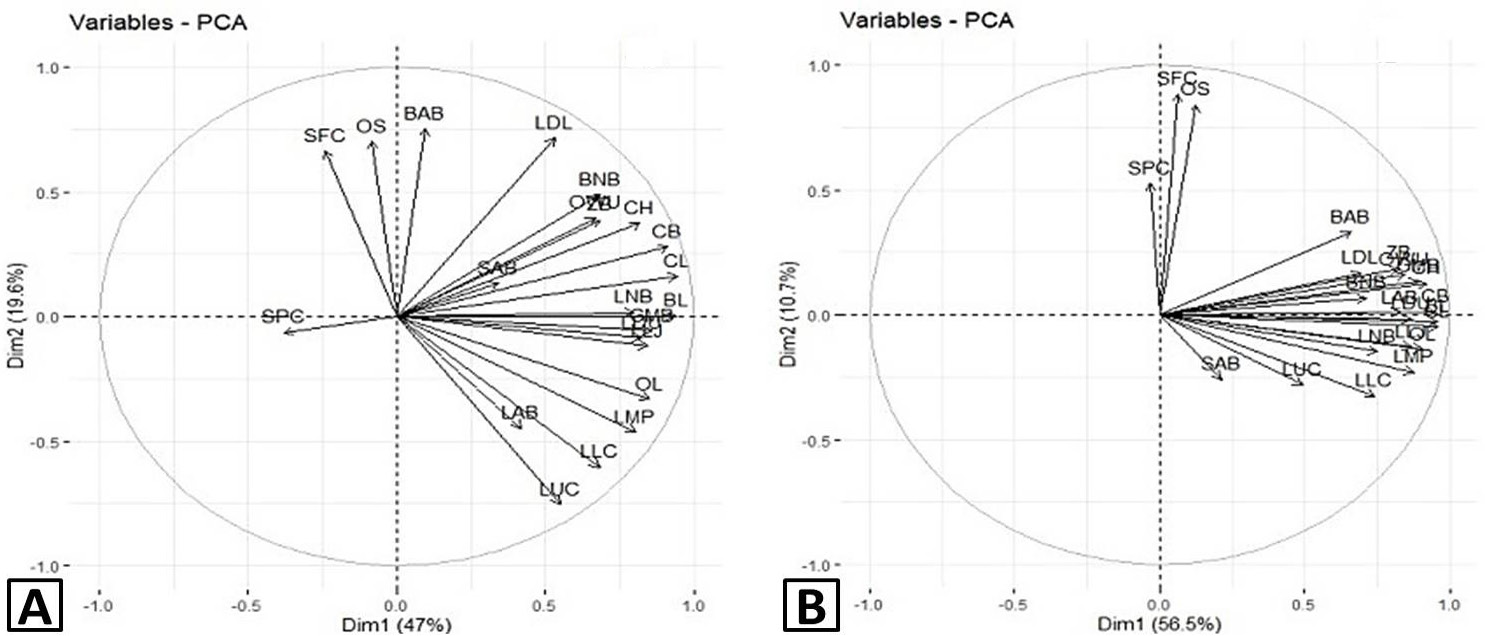
Correlations between variables and the first two principal components. A, male; B, female.
The box plots of zygomatic breadth among four zokor species. A, males; B, females.