Effects of Moringa oleifera, Curcumin, and Green Tea Extracts on Histopathological Changes in Mesenteric Lymph Nodes and Spleen of Albino Rats with Benzene-Induced Leukemia
Effects of Moringa oleifera, Curcumin, and Green Tea Extracts on Histopathological Changes in Mesenteric Lymph Nodes and Spleen of Albino Rats with Benzene-Induced Leukemia
Ahmed Alazzouni1, Ashraf Al-Brakati2,*, Sherif Rabie1, Mohamed Gabry1 and Basmaa Hassan1
Photomicrographs of the negative control group showing: A, normal mesenteric lymph node structure with cortex (C), paracortex (PC), and medulla (M) (×100); B, cortex with lymphoid follicle (LF), germinal center (GC), capsule (Cap), cortical sinuses (CS), and subcapsular sinus (SCS) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, normal spleen structure with white pulp (WP) or lymphoid follicles (LF), vascular red pulp (RP), outer capsule (C), and trabeculae (T) (×100); E, white pulp’s LFs with germinal center (GC), periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), central arteriole (CA), and marginal zone (MZ) (×400); F, red pulp (RP) with splenic cords (SC) and venous sinuses (VS) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, normal thin delicate elastic fibers in lymph node cortex (arrow) (×400); H, normal thin delicate elastic fibers in spleen RP (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); I, normal number of flattened mast cells (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
Photomicrographs of the benzene-injected group showing: A, whole lymph node structure (×100); B, cortical changes with some necrotic (ghost) cells (arrow), dilated, congested cortical sinus (CS), and non-active lymphoid follicles (LF) (×400); C, medullary changes with dilated and congested high endothelial venules (HEVs) lined with simple squamous epithelium (arrow) (×400); D, spleen with dilated congested pulp artery (PA) (×100); E, white pulp (WP) with thick dilated central arteriole (CA) in non-active LF (×400); F, red pulp (RP) with congested venous sinuses (VS) and dilated PA (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, densely stained irregular thick elastic fibers (arrow) (×400); H, thick elastic fiber aggregation in the spleen (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); I, increased numbers and larger than normal mast cells (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
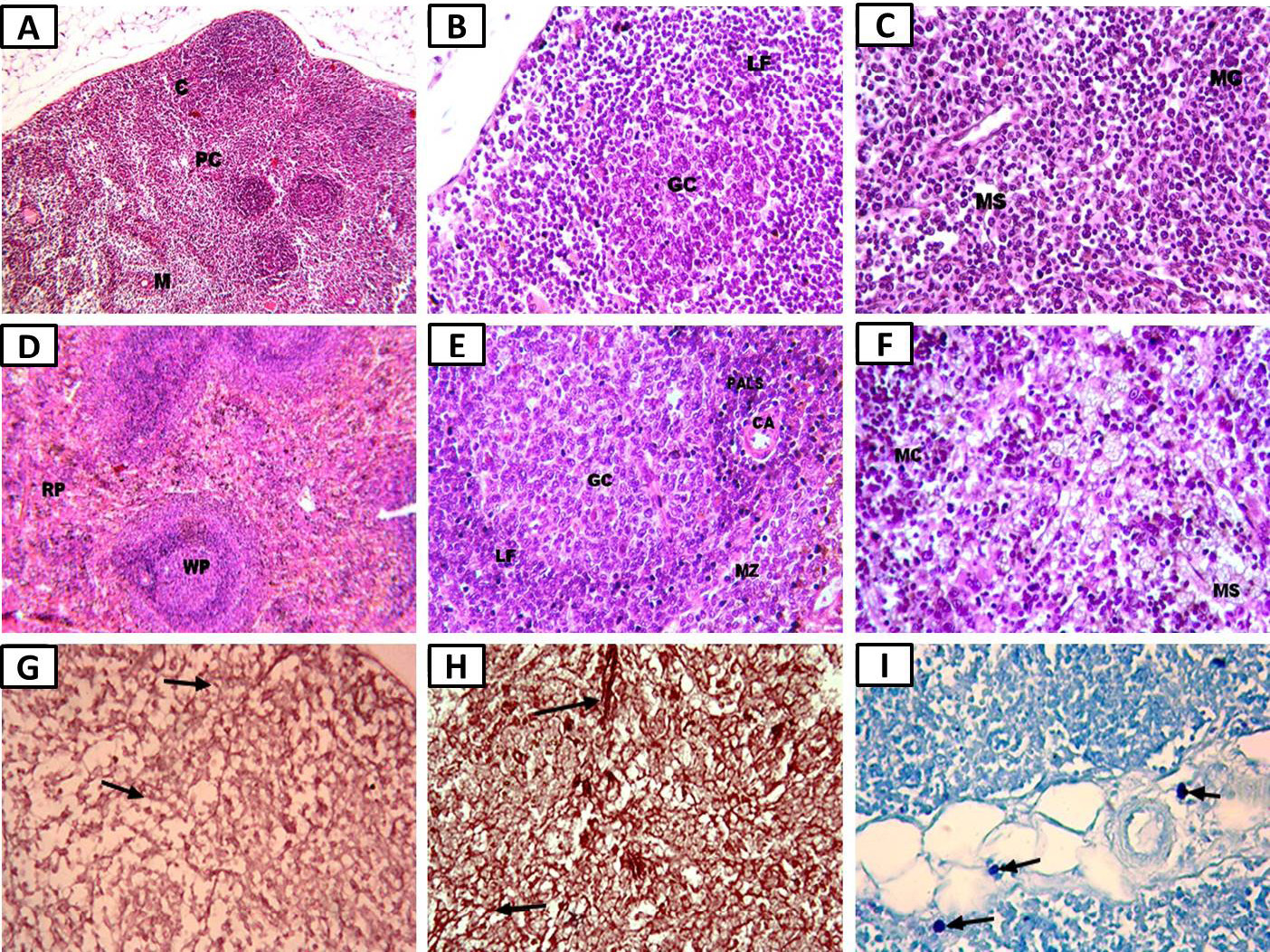
Photomicrographs of the M. oleifera treatment group showing: A, marked improvement in lymph node structure with cortex (C), paracortex (PC), and medulla (M) (×100); B, cortical lymphoid follicle (LF) with germinal center (GC) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, marked improvement in spleen white pulp (WP) and red pulp (RP) structure (×100); E, WP with LF, central arteriole (CA), periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), GC, and marginal zone (MZ) (×400); F, RP with splenic cords (SC) and venous sinuses (VS) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, almost normal shape of thin, delicate elastic fibers in the lymph node (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); H, nearly normal shape of thin, elastic fibers (arrow) in the spleen (Orcein, ×400); I, almost normal mast cell size and numbers (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
Photomicrographs of the curcumin treatment group showing: A, marked improvement in lymph node structure with cortex (C), paracortex (PC), and medulla (M) (×100); B, cortical lymphoid follicle (LF) with germinal center (GC) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, marked improvement in spleen white pulp (WP) and red pulp (RP) structure (×100); E, WP with LF, central arteriole (CA), periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), GC, and marginal zone (MZ) (×400); F, RP with splenic cords (SC) and venous sinuses (VS) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, almost normal shape of thin, delicate elastic fibers in the lymph node (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); H, nearly normal shape of thin, elastic fibers (arrow) in the spleen (Orcein, ×400); I, almost normal mast cell size and numbers (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
Photomicrographs of the green tea treatment group showing: A, marked improvement in lymph node structure with cortex (C), paracortex (PC), and medulla (M) (×100); B, cortical lymphoid follicle (LF) with germinal center (GC) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, marked improvement in spleen white pulp (WP) and red pulp (RP) structure (×100); E, WP with LF, central arteriole (CA), periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), GC, and marginal zone (MZ) (×400); F, RP with splenic cords (SC) and venous sinuses (VS) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, almost normal shape of thin, delicate elastic fibers in the lymph node (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); H, nearly normal shape of thin, elastic fibers (arrow) in the spleen (Orcein, ×400); I, almost normal mast cell size and numbers (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
Photomicrographs of the combined curcumin and green tea extract treatment group showing: A, obvious improvement in lymph node structure with cortex (C), paracortex (PC), and medulla (M) (×100); B, cortical lymphoid follicle (LF) with germinal center (GC) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, obvious improvement in spleen white pulp (WP) and red pulp (RP) structure (×100); E, WP with LF, central arteriole (CA), periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), GC, and marginal zone (MZ) (×400); F, RP with splenic cords (SC) and venous sinuses (VS) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, almost normal shape of thin, delicate elastic fibers in the lymph node (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); H, nearly normal shape of thin, elastic fibers (arrow) in the spleen (Orcein, ×400); I, almost normal mast cell size and numbers (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).
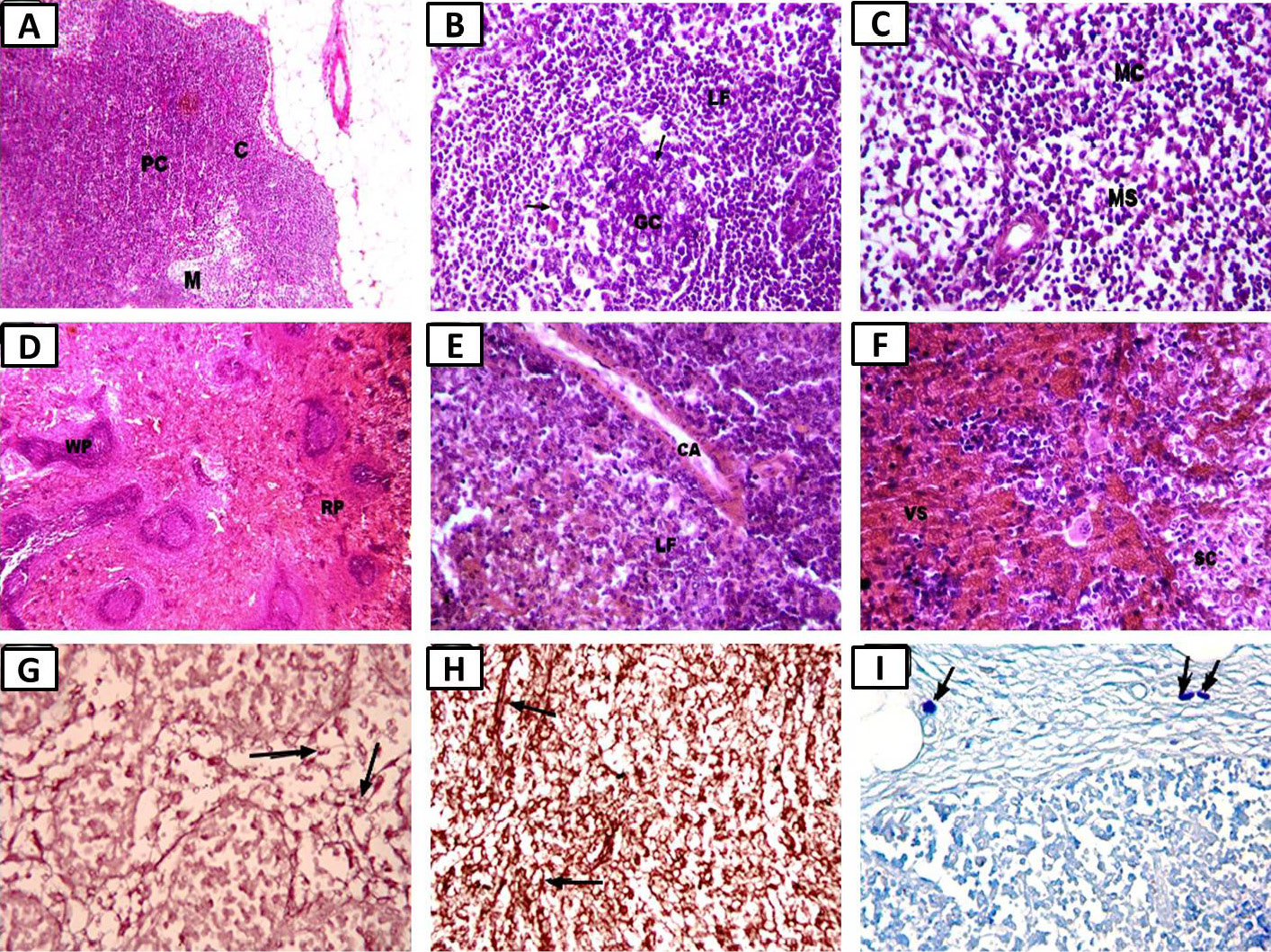
Photomicrographs of the cyclophosphamide treatment group showing: A, slight improvement in the whole structure of the lymph node (×100); B, cortical changes with some lymphocytic depletion in germinal centers and some necrotic degenerated cells (ghost cell) (arrows) (×400); C, medulla with medullary cords (MC) and medullary sinuses (MS) (×400); D, slight improvement in spleen white pulp and red pulp structure (×100); E, white pulp with dilated central arteriole (CA) in non-active lymphoid follicle (LF) (×400); F, red pulp with dilated and congested venous sinuses (VS) and splenic cords (SC) (hematoxylin and eosin, ×400); G, almost normal shape of thin, delicate elastic fibers in the lymph node (arrow) (Orcein, ×400); H, nearly normal shape of thin, elastic fibers (arrow) in the spleen (Orcein, ×400); I, almost normal mast cell size and numbers (arrows) in the pericapsular connective tissue of the lymph node (toluidine blue, ×400).