Streptococcus iniae: A Growing Threat and Causative Agent of Disease Outbreak in Farmed Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis)
Streptococcus iniae: A Growing Threat and Causative Agent of Disease Outbreak in Farmed Chinese Sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis)
Murtala Muhammad, Ting Zhang, Siyu Gong, Jing Bai, Jiansong Ju, Baohua Zhao* and Dong Liu*
Phylogenetic tree constructed based on 16S rRNA gene sequence. The isolates were indicated by accession number, strain names, and country of isolation.
Scanning Electron microscopic images of S. iniae HNM-1, Colonies were arranged in chains and in community, partially observed extracellular matrix-like structure of Biofilm can be observed.
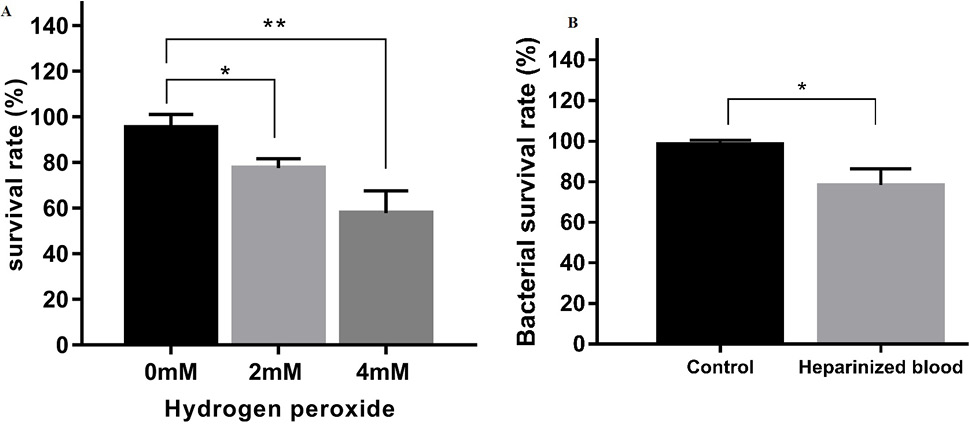
Virulence of S. iniae HNM-1. (A) Percentage survival of S. iniae HNM-1 strain incubated in H2O2. The bacteria has a survival rate of 77%. (B) Percentage of CFUs after 2 hours of incubation at 350C in heparinized fish blood.
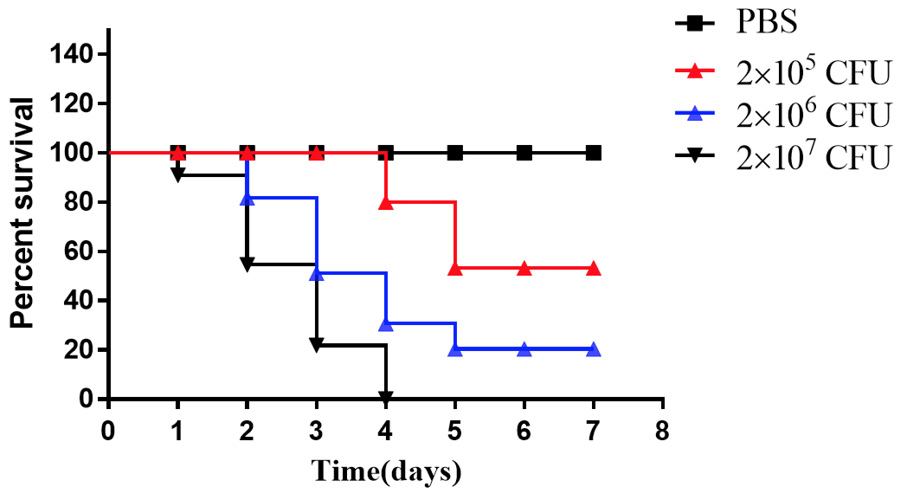
Percent survival of A. sinensis challenged with different concentrations of S. iniae HNM-1.
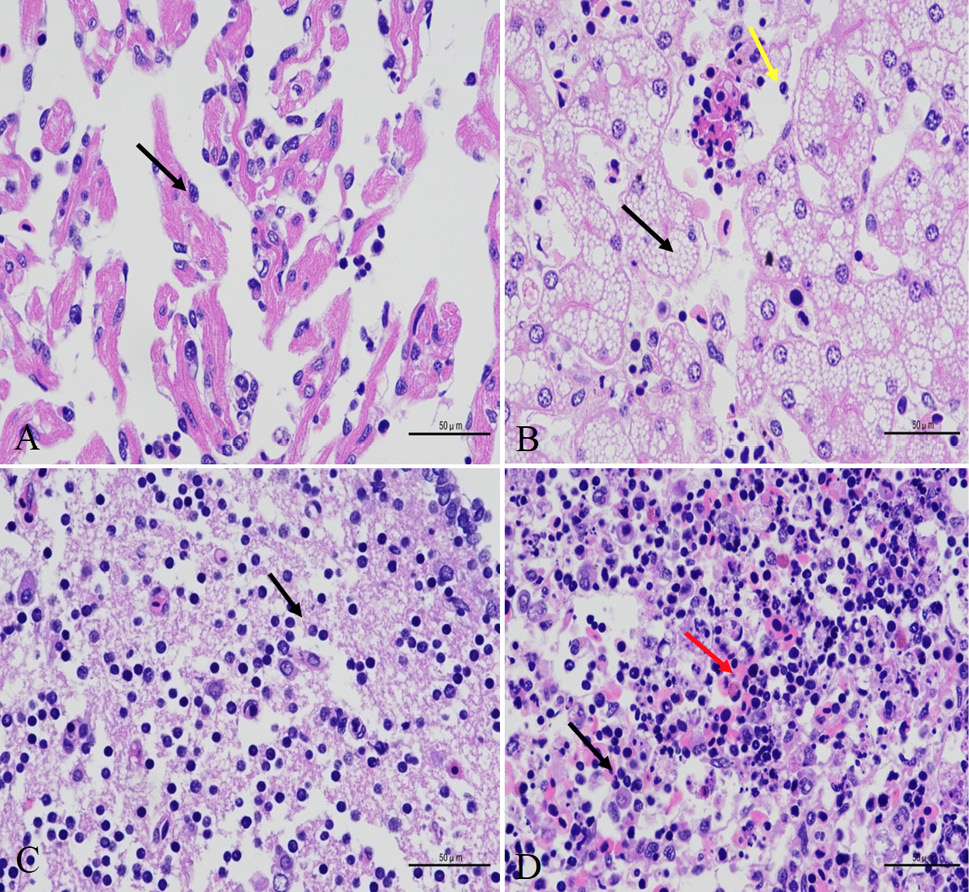
Lesions observed in organs of Chinese sturgeon infected by S. iniae. The primary lesions in the heart include interstitial edema, enlargement of stroma as well as thickening of the pericardium (A). In the liver, hepatocytes were characterized by steatosis (B). Brain structure is disorganized with swollen and loose tissues (C). In the spleen, the boundaries of red and white pulps were unclear as well as splenic lymphocyte necrosis (D).